## About The Project
It all started with a DropBox observation. Link to the [comment](http://paranoia.dubfire.net/2011/04/how-dropbox-sacrifices-user-privacy-for.html?showComment=1302661727678). Some users experienced a lot less time when uploading files to DropBox. This was because DropBox was able to detect duplicate files and only uploaded the new file. The schema can be seen below.
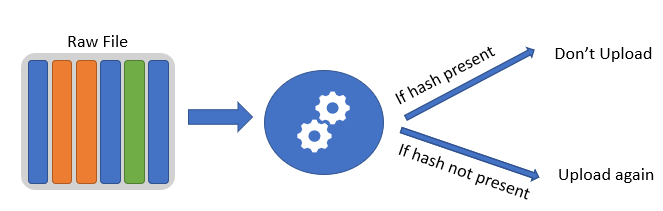
This can be extended to another design where rather than taking entire file we can break file into chunks and store them in a database. Duplicates need not be stored. Only single copy is sufficient. We design 2 functions. `save_file` and `load_file`
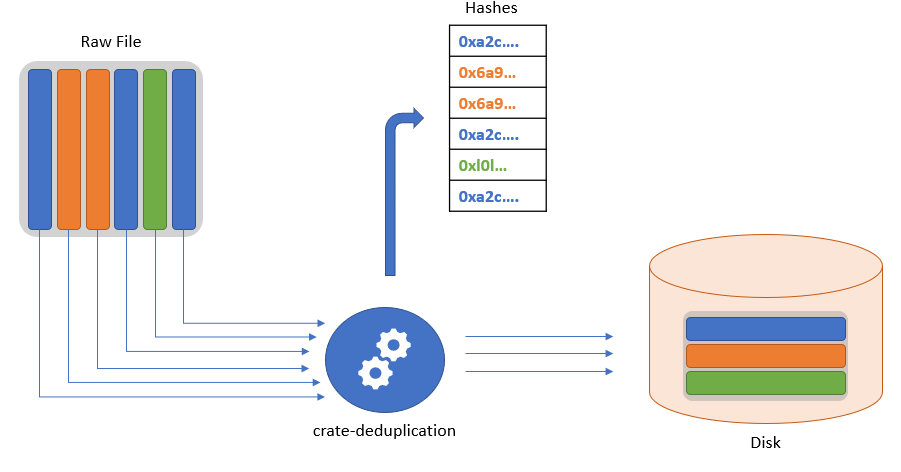
### `save_file`
This function takes `filename` as an argument and saves the file into storage. The function breaks the file into chunks and removes duplicate chunks. If a chunk is already present it need not store the copy.
The schema can be seen below.
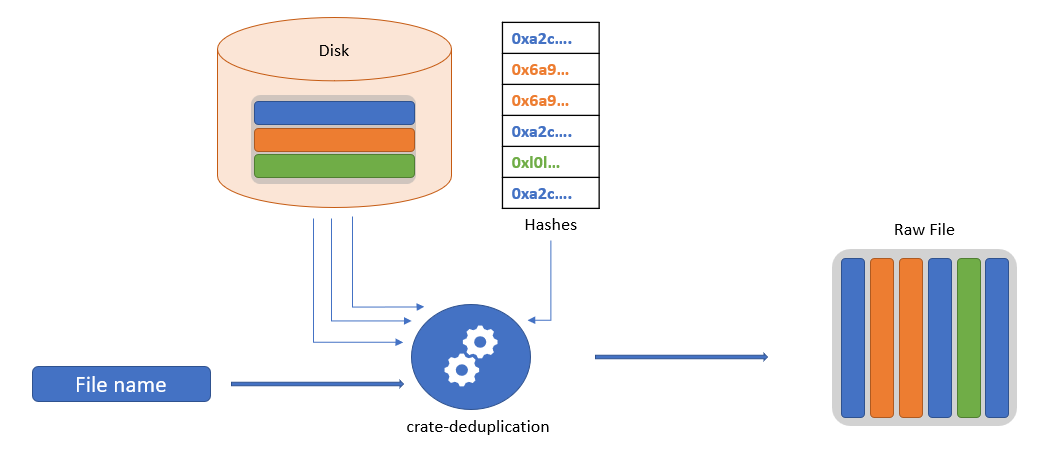
### `load_file`
This function takes `filename` as an argument and loads the file from storage. The function collects all the chunks and combines them to form the file. The schema can be seen below.
## Getting Started
The library is made entirely in rust. You need to install rust to use this library and packages mentioned in the `Cargo.toml` file.
### Prerequisites
Install rust from [here](https://www.rust-lang.org/tools/install)
### Installation
1. Clone the repo
```sh
git clone https://github.com/anirudhakulkarni/de-duplication.git
```
2. Install Rust packages
```sh
cargo build
```
## Usage
The library provides 2 main functions, `save_file` and `load_file`. The `save_file` function takes a file path and saves the file in the storage. The `load_file` function takes a file path and loads the file from the storage. `load_file` loads file in vector of bytes.
Example usage:
```rust
use de_duplication::deduplication::save_file;
use de_duplication::deduplication::load_file;
fn main() {
let file_path = "test.txt";
// writing 1,2,3,4,5 to the file
let mut file = File::create(file_path).unwrap();
file.write_all(b"1,2,3,4,5").unwrap();
file.sync_all().unwrap();
// saving the file to the storage
save_file(file_path);
let file = load_file(file_path);
assert_eq!(file, vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);
}
```
A more comprehensive use can be done by wrapping the entire thing in a struct:
Refer to
[dedup.rs](
https://github.com/anirudhakulkarni/Live-Snapshot/blob/main/src/vmm/src/dedup.rs
)
to create the struct. Then refer to
[lib.rs](
https://github.com/anirudhakulkarni/Live-Snapshot/blob/main/src/vmm/src/lib.rs
) to see how the functions are used.
## Results
We deploy this library to our snapshot and restore server which allows us to spawn multiple VMs and pause/resume them at wish. The library is used to manage the snapshots efficiently. The results are as follows:
### Overall result:
We handled 150 snapshots of 256MB each. The total size of the snapshots was 38GB. The total size of the snapshots after de-duplication was 2.5GB. This is a 15x improvement in storage efficiency.
The snapshots were taken at arbitrary point in VM executation, still the library was able to de-duplicate the files efficiently.
### Total size taken to save a file:
Chunk size plays important role in the efficiency of the library. We tested the library with different chunk sizes. The results are as follows:
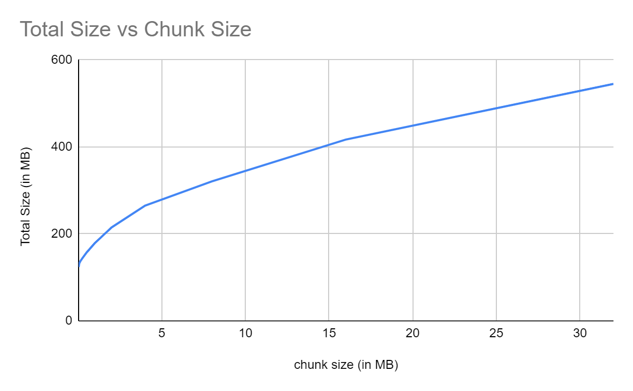
We see a linear increase in net size with increase in chunk size. This is because the library is able to de-duplicate the files less efficiently with larger chunk size.
### Time taken to save a file:
As the chunk size decreased, number of chunks increased. This increased the time taken to save and load the file. The results are as follows:
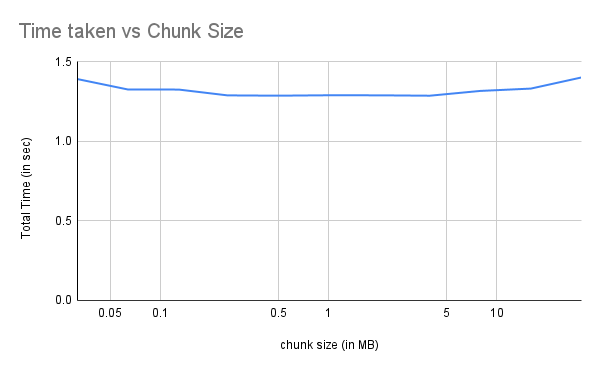
Note the logrithmic scale on the y-axis. We see a linear increase in time taken to save the file due to hashing overhead.
### Tradeoff between time and space:
Extreme examples of chunk size trade-off are 1 byte and 1GB. The later is inefficient as the library is not able to de-duplicate the files at all. The former is inefficient as the library is not able to de-duplicate the files efficiently.
## Roadmap
- [x] Deduplication Library
- [ ] Modify the storage to use a database
## Contributing
Contributions are what make the open source community such an amazing place to learn, inspire, and create. Any contributions you make are **greatly appreciated**.
If you have a suggestion that would make this better, please fork the repo and create a pull request. You can also simply open an issue with the tag "enhancement".
Don't forget to give the project a star! Thanks again!
1. Fork the Project
2. Create your Feature Branch (`git checkout -b feature/AmazingFeature`)
3. Commit your Changes (`git commit -m 'Add some AmazingFeature'`)
4. Push to the Branch (`git push origin feature/AmazingFeature`)
5. Open a Pull Request