[![GitHub All Releases][release-img]][release]
[![Build][workflow-img]][workflow]
[![Issues][issues-img]][issues]
[![Crates][crates-img]][crates]
[![License: MIT][license-img]][license]
[crates]: https://crates.io/crates/deoptimizer
[crates-img]: https://img.shields.io/crates/v/deoptimizer
[release]: https://github.com/EgeBalci/deoptimizer/releases
[release-img]: https://img.shields.io/github/v/release/EgeBalci/deoptimizer
[downloads]: https://github.com/EgeBalci/deoptimizer/releases
[downloads-img]: https://img.shields.io/github/downloads/EgeBalci/deoptimizer/total?logo=github
[issues]: https://github.com/EgeBalci/deoptimizer/issues
[issues-img]: https://img.shields.io/github/issues/EgeBalci/deoptimizer?color=red
[license]: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EgeBalci/deoptimizer/master/LICENSE
[license-img]: https://img.shields.io/github/license/EgeBalci/deoptimizer.svg
[google-cloud-shell]: https://console.cloud.google.com/cloudshell/open?git_repo=https://github.com/EgeBalci/deoptimizer&tutorial=README.md
[workflow-img]: https://github.com/EgeBalci/deoptimizer/actions/workflows/main.yml/badge.svg
[workflow]: https://github.com/EgeBalci/deoptimizer/actions/workflows/main.yml
[moneta-ref]: https://github.com/forrest-orr/moneta
[pe-sieve-ref]: https://github.com/hasherezade/pe-sieve
[insomnihack]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Issvbst_89I
[havoc]: https://github.com/HavocFramework/Havoc
This tool is a machine code de-optimizer. By transforming/mutating the machine code instructions to their functional equivalents it makes possible to bypass pattern-based detection mechanisms used by security products.
## Why?
Bypassing security products is a very important part of many offensive security engagements. The majority of the current AV evasion techniques used in various different evasion tools, such as packers, shellcode encoders, and obfuscators, are dependent on the use of self-modifying code running on RWE memory regions. Considering the current state of security products, such evasion attempts are easily detected by memory analysis tools such as [Moneta](https://github.com/forrest-orr/moneta) and [Pe-sieve](https://github.com/hasherezade/pe-sieve). This project introduces a new approach to code obfuscation with the use of machine code de-optimization. It uses certain mathematical approaches, such as arithmetic partitioning, logical inverse, polynomial transformation, and logical partitioning, for transforming/mutating the instructions of the target binary without creating any recognizable patterns. The tool is capable of transforming the instructions of a given binary up to ~95% by using the mentioned de-optimization tricks.
**Watch the presentation for more...**
- [Why So Optimized? - Insomni'hack 2024](https://youtu.be/Issvbst_89I?feature=shared)
## Installation
**Download the pre-built release binaries [HERE](https://github.com/EgeBalci/deoptimizer/releases).**
[](https://console.cloud.google.com/cloudshell/open?git_repo=https://github.com/EgeBalci/deoptimizer&tutorial=README.md)
***From Source***
```
cargo install deoptimizer
```
***Docker Install***
[](https://hub.docker.com/r/egee/deoptimizer/)
```bash
docker run -it egee/deoptimizer -h
```
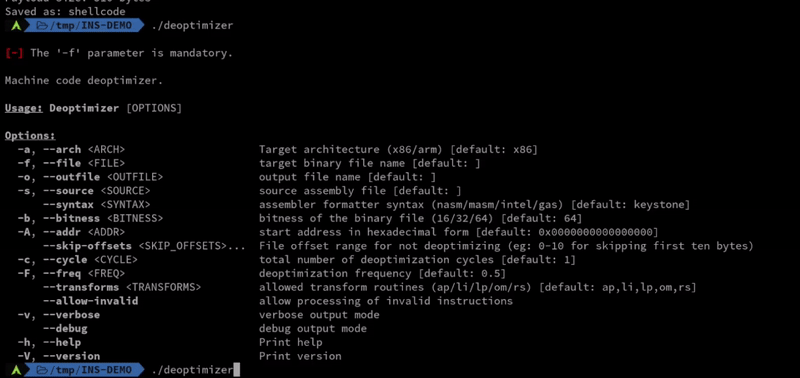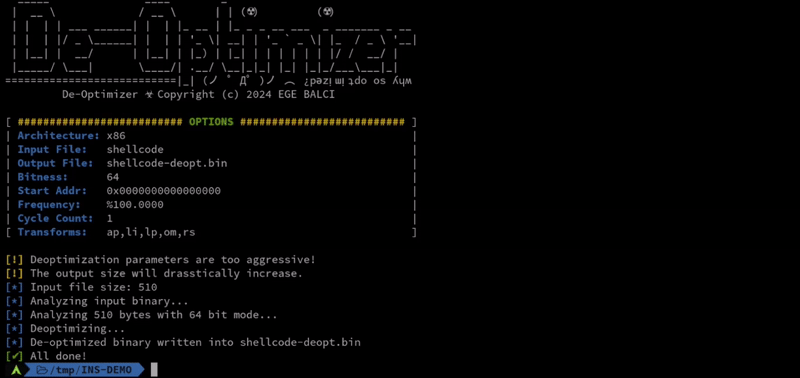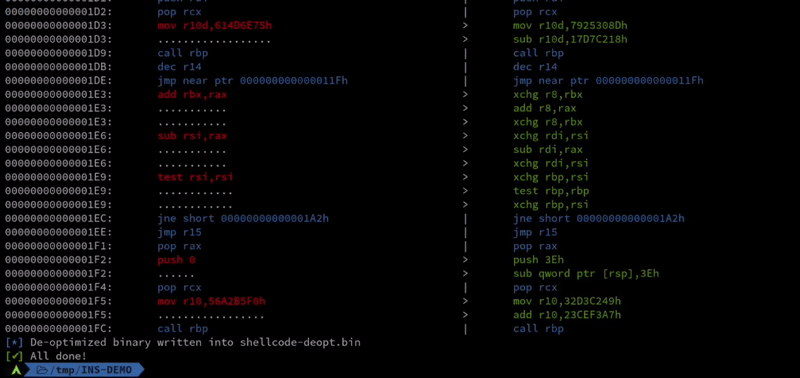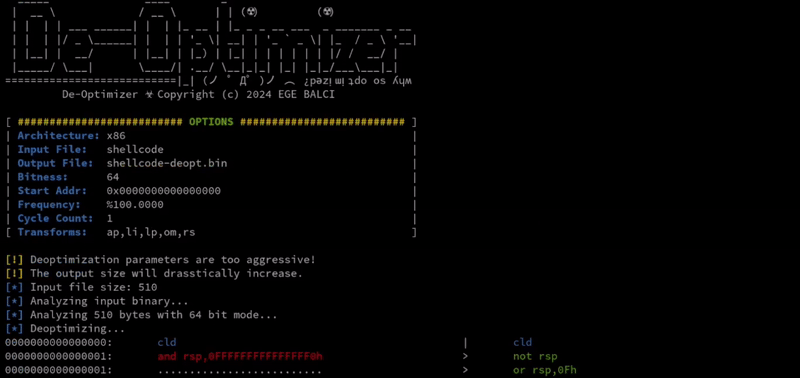
## Usage
> [!WARNING]
> This project is still in the development stage! The available transform gadgets, functions, and command line parameter names may be adjusted, backward compatibility is not guaranteed.