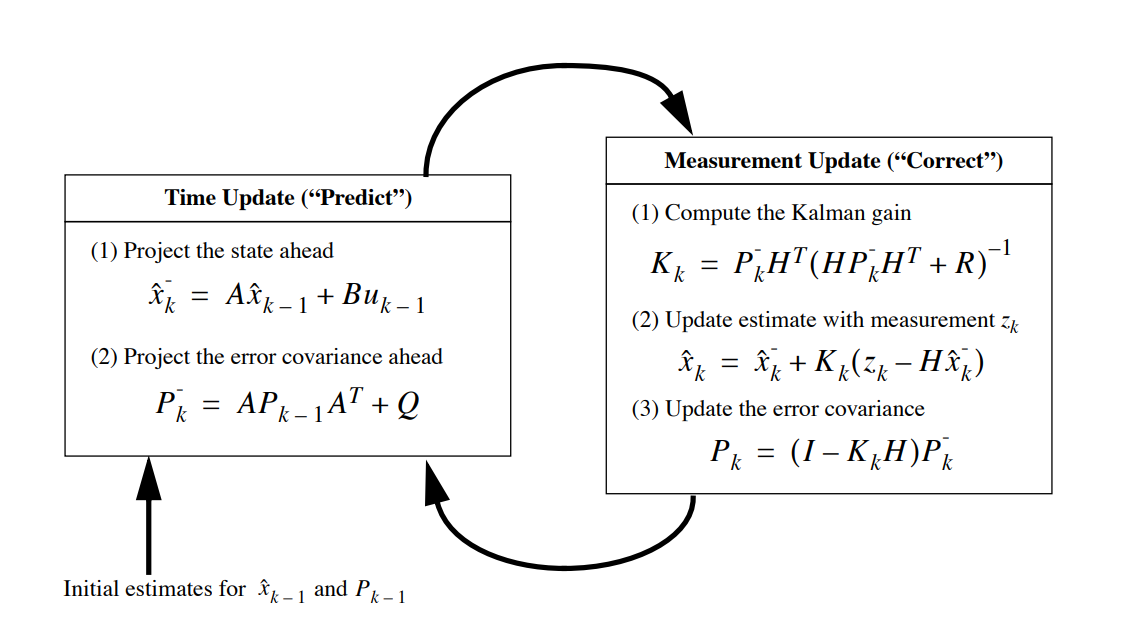

Fig 1. Operation of the Kalman filter. Welch & Bishop, 'An Introduction to the Kalman Filter'
## 1-D Kalman filter Considering acceleration motion let's write down its equations: Velocity: $$v = v_{0} + at \tag{11}$$ $$v(t) = x'(t) $$ $$a(t) = v'(t) = x''(t)$$ Position: $$x = x_{0} + v_{0}t + \frac{at^2}{2} \tag{12}$$ Let's write $(11)$ and $(12)$ in Lagrange form: $$x'_ {k} = x'_ {k-1} + x''_{k-1}\Delta t \tag{13}$$ $$x_{k} = x_{k-1} + x'_ {k-1}\Delta t + \frac{x''_{k-1}(\Delta t^2)}{2} \tag{14}$$ State vector $\chi_{k}$ looks like: $$\chi_{k} = \begin{bmatrix} x_{k} \\ x'_ {k} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} x_{k-1} + x'_ {k-1}\Delta t + \frac{x''_ {k-1}(\Delta t^2)}{2} \\ x'_ {k-1} + x''_{k-1}\Delta t \end{bmatrix} \tag{15}$$ Matrix form of $\chi_{k}$ : $$\chi_{k} = \begin{bmatrix} x_{k} \\ x'_ {k} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & \Delta t \\ 0 & 1\end{bmatrix} ⋅ \begin{bmatrix} x_{k-1} \\ x'_ {k-1} \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \\ \Delta t \end{bmatrix} ⋅ x''_ {k-1} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & \Delta t \\ 0 & 1\end{bmatrix} ⋅ \chi_{k-1} + \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \\ \Delta t \end{bmatrix} ⋅ x''_{k-1} \tag{16}$$ Taking close look on $(16)$ and $(1)$ we can write transition matrix $A$ and control input matrix $B$ as follows: $$A = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & \Delta t \\ 0 & 1\end{bmatrix} \tag{17}$$ $$B = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \\ \Delta t \end{bmatrix} \tag{18}$$ Let's find transformation matrix $H$. According to $(2)$: $$z_{k} = H⋅\chi_{k} + v_{k} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix} ⋅\begin{bmatrix} x_{k} \\ {x'_ {k}} \end{bmatrix} + v_{k} \tag{19}$$ $$ H = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \tag{20}$$ __Notice:__ $v_{k}$ __in__ $(19)$ __- is not speed, but measurement noise! Don't be confused with notation. E.g.:__ $$ \text{$ \chi_{k} = \begin{bmatrix} 375.74 \\ 0 - \text{assume zero velocity} \end{bmatrix} $, $ v_{k} = 2.64 => $} $$ $$ \text{$ => z_{k} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix} ⋅\begin{bmatrix} 375.74 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} + 2.64 = \begin{bmatrix} 378.38 & 2.64 \end{bmatrix} $ - you can see that first vector argument it is just noise $v_{k}$ added}$$ $$ \text{to observation $x_{k}$ and the second argument is noise $v_{k}$ itself.}$$ Process noise covariance matrix $Q$: $$Q = \begin{matrix} & \begin{matrix}x && x'\end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix}x \\ x'\end{matrix} & \begin{bmatrix} \sigma^2_{x} & \sigma_{x} \sigma_{x'} \\ \sigma_{x'} \sigma_{x} & \sigma^2_{x'}\end{bmatrix} \\\\ \end{matrix} \tag{21}$$ $$\text{, where} $$ $$ \text{$\sigma_{x}$ - standart deviation of position} $$ $$ \text{$\sigma_{x'}$ - standart deviation of velocity} $$ Since we know about $(14)$ we can define $\sigma_{x}$ and $\sigma_{x'}$ as: $$ \sigma_{x} = \sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \tag{22}$$ $$ \sigma_{x'} = \sigma_{x''} \Delta t \tag{23}$$ $$\text{, where $\sigma_{x''}$ - standart deviation of acceleration (tuned value)} $$ And now process noise covariance matrix $Q$ could be defined as: $$ Q = \begin{bmatrix} (\sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & \sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \sigma_{x''} \Delta t \\ \sigma_{x''} \Delta t \sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} & (\sigma_{x''} \Delta t)^2 \end{bmatrix} = $$ $$ = \begin{bmatrix} (\sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & (\sigma_{x''})^2 \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \Delta t \\ (\sigma_{x''})^2 \Delta t \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} & (\sigma_{x''} \Delta t)^2 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} (\frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \Delta t \\ \Delta t \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} & \Delta t^2 \end{bmatrix} \sigma^2_{x''}$$ $$ = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^4}{4} & \frac{\Delta t^3}{2} \\ \frac{\Delta t^3}{2} & \Delta t^2 \end{bmatrix} \sigma^2_{x''} \tag{24}$$ $$ \text{Assuming that $x''$ - is acceleration $a$, $Q = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^4}{4} & \frac{\Delta t^3}{2} \\ \frac{\Delta t^3}{2} & \Delta t^2 \end{bmatrix} \sigma^2_{a}$} \tag{25}$$ Covariance of measurement noise $R$ is scalar (matrix of size $1 \times 1$) and it is defined as variance of the measurement noise: $$R = \begin{matrix} \begin{matrix}& x\end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix}x\end{matrix} \begin{bmatrix}\sigma^2_{z}\end{bmatrix} \\\\ \end{matrix} = \sigma^2_{z} \tag{26}$$ Rust implementation is [here](./src/kalman/kalman_1d.rs#L4) Example of usage: ```rust let dt = 0.1; let u = 2.0; let std_dev_a = 0.25; let std_dev_m = 1.2; let t: nalgebra::SVector:: ## 2-D Kalman filter
Considering acceleration motion again let's write down its equations:
Considering the same physical model as in $(13)$ - $(14)$ let's write down state vector $\chi_{k}$:
$$\chi_{k} = \begin{bmatrix}
x_{k} \\
y_{k} \\
x'_ {k} \\
y'_ {k} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}
x_{k-1} + x'_ {k-1}\Delta t + \frac{x''_ {k-1}(\Delta t^2)}{2} \\
y_{k-1} + y'_ {k-1}\Delta t + \frac{y''_ {k-1}(\Delta t^2)}{2} \\
x'_ {k-1} + x''_ {k-1}\Delta t \\
y'_ {k-1} + y''_ {k-1}\Delta t
\end{bmatrix} \tag{27}$$
Matrix form of $\chi_{k}$ :
$$\chi_{k} = \begin{bmatrix} x_{k} \\
y_{k} \\
x'_ {k} \\
y'_ {k}
\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & \Delta t & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 0 & \Delta t \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} ⋅ \begin{bmatrix} x_{k-1} \\
y_{k-1} \\
x'_ {k-1} \\
y'_ {k-1} \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} & 0 \\
0 & \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \\
\Delta t & 0 \\
0 & \Delta t \end{bmatrix} ⋅ \begin{bmatrix} x''_ {k-1} \\
y''_ {k-1} \end{bmatrix} = $$
$$ = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & \Delta t & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 0 & \Delta t \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} ⋅ \chi_{k-1} + \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} & 0 \\
0 & \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \\
\Delta t & 0 \\
0 & \Delta t \end{bmatrix} ⋅ \begin{bmatrix} x''_ {k-1} \\
y''_{k-1} \end{bmatrix} \tag{28}$$
$$ \text{Assuming that $x''$ and $y''$ - is acceleration $a$, }$$
$$ a_{k-1} = \begin{bmatrix} x''_ {k-1} \\
y''_{k-1} \end{bmatrix} \tag{29}$$
$$\chi_{k} = \begin{bmatrix} x_{k} \\
y_{k} \\
x'_ {k} \\
y'_ {k}
\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & \Delta t & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 0 & \Delta t \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} ⋅ \chi_{k-1} + \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} & 0 \\
0 & \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \\
\Delta t & 0 \\
0 & \Delta t \end{bmatrix} ⋅ a_{k-1} \tag{30}$$
Taking close look on $(16)$ and $(1)$ we can write transition matrix $A$ and control input matrix $B$ as follows:
$$A = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & \Delta t & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 0 & \Delta t \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \tag{31}$$
$$B = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} & 0 \\
0 & \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \\
\Delta t & 0 \\
0 & \Delta t \end{bmatrix} \tag{32}$$
Let's find transformation matrix $H$. According to $(2)$ and $(19)$ - $(20)$:
$$z_{k} = H⋅\chi_{k} + v_{k} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} ⋅\begin{bmatrix} x_{k} \\
y_{k} \\
{x'_ {k}} \\
{y'_ {k}} \end{bmatrix} + v_{k} \tag{33}$$
$$ H = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \tag{34}$$
Process noise covariance matrix $Q$:
$$Q = \begin{matrix}
& \begin{matrix}x && y && x' && y'\end{matrix} \\
\begin{matrix}x \\
y \\
x' \\
y'\end{matrix} &
\begin{bmatrix} \sigma^2_{x} & 0 & \sigma_{x} \sigma_{x'} & 0 \\
0 & \sigma^2_{y} & 0 & \sigma_{y} \sigma_{y'} \\
\sigma_{x'} \sigma_{x} & 0 & \sigma^2_{x'} & 0 \\
0 & \sigma_{y'} \sigma_{y} & 0 & \sigma^2_{y'}\end{bmatrix}
\\\\
\end{matrix} \tag{35}$$
$$\text{, where} $$
$$ \text{$\sigma_{x}$ - standart deviation of position for $x$ component} $$
$$ \text{$\sigma_{y}$ - standart deviation of position for $y$ component} $$
$$ \text{$\sigma_{x'}$ - standart deviation of velocity for $x$ component} $$
$$ \text{$\sigma_{y'}$ - standart deviation of velocity for $y$ component} $$
Since we know about $(14)$ we can define $\sigma_{x}$, $\sigma_{y}$, $\sigma_{x'}$ and $\sigma_{y'}$ as:
$$ \sigma_{x} = \sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \tag{36}$$
$$ \sigma_{y} = \sigma_{y''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \tag{37}$$
$$ \sigma_{x'} = \sigma_{x''} \Delta t \tag{38}$$
$$ \sigma_{y'} = \sigma_{y''} \Delta t \tag{39}$$
$$\text{, where $\sigma_{x''}$ and $\sigma_{y''}$ - standart deviation of acceleration (tuned values)} $$
And now process noise covariance matrix $Q$ could be defined as:
$$ Q = \begin{bmatrix} (\sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & 0 & \sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \sigma_{x''} \Delta t & 0 \\
0 & (\sigma_{y''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & 0 & \sigma_{y''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \sigma_{y''} \Delta t \\
\sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \sigma_{x''} \Delta t & 0 & (\sigma_{x''} \Delta t)^2 & 0 \\
0 & \sigma_{y''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \sigma_{y''} \Delta t & 0 & (\sigma_{y''} \Delta t)^2 \end{bmatrix} = $$
$$ = \begin{bmatrix} (\sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & 0 & (\sigma_{x''})^2 \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \Delta t & 0 \\
0 & (\sigma_{y''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & 0 & (\sigma_{y''})^2 \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \Delta t \\
(\sigma_{x''})^2 \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \Delta t & 0 & (\sigma_{x''} \Delta t)^2 & 0 \\
0 & (\sigma_{y''})^2 \frac{\Delta t^2}{2}\Delta t & 0 & (\sigma_{y''} \Delta t)^2 \end{bmatrix} = \text{| Knowing that $x''$ and $y''$ - acceleration|} = $$
$$ = \begin{bmatrix} (\frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & 0 & \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \Delta t & 0 \\
0 & (\frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & 0 & \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \Delta t \\
\frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \Delta t & 0 & \Delta t^2 & 0 \\
0 & \Delta t \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} & 0 & \Delta t^2 \end{bmatrix} \sigma^2_{a''}$$
$$ = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^4}{4} & 0 & \frac{\Delta t^3}{2} & 0 \\
0 & \frac{\Delta t^4}{4} & 0 & \frac{\Delta t^3}{2} \\
\frac{\Delta t^3}{2} & 0 & \Delta t^2 & 0 \\
0 & \frac{\Delta t^3}{2} & 0 & \Delta t^2 \end{bmatrix} \sigma^2_{a''} \tag{40}$$
Covariance of measurement noise $R$ is matrix of size $2 \times 2$ (since there are two components - $x$ and $y$) and it is defined as variance of the measurement noise:
$$R = \begin{matrix}
\begin{matrix}& x & y\end{matrix} \\
\begin{matrix}x \\
y \end{matrix}
\begin{bmatrix}\sigma^2_{x} & 0 \\
0 & \sigma^2_{y} \end{bmatrix}
\\\\
\end{matrix} = \begin{bmatrix}\sigma^2_{x} & 0 \\
0 & \sigma^2_{y} \end{bmatrix} \tag{41}$$
Rust implementation is [here](./src/kalman/kalman_2d.rs#L4)
Example of usage:
```rust
let dt = 0.04; // 1/25 = 25 fps - just an example
let ux = 1.0;
let uy = 1.0;
let std_dev_a = 2.0;
let std_dev_mx = 0.1;
let std_dev_my = 0.1;
// Sample measurements
// Note: in this example Y-axis going from up to down
let xs = vec![311, 312, 313, 311, 311, 312, 312, 313, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 311, 311, 311, 311, 311, 310, 311, 311, 311, 310, 310, 308, 307, 308, 308, 308, 307, 307, 307, 308, 307, 307, 307, 307, 307, 308, 307, 309, 306, 307, 306, 307, 308, 306, 306, 306, 305, 307, 307, 307, 306, 306, 306, 307, 307, 308, 307, 307, 308, 307, 306, 308, 309, 309, 309, 309, 308, 309, 309, 309, 308, 311, 311, 307, 311, 307, 313, 311, 307, 311, 311, 306, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312];
let ys = vec![5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 12, 12, 13, 16, 16, 18, 18, 19, 19, 20, 20, 22, 22, 23, 23, 24, 24, 28, 30, 32, 35, 39, 42, 44, 46, 56, 58, 70, 60, 52, 64, 51, 70, 70, 70, 66, 83, 80, 85, 80, 98, 79, 98, 61, 94, 101, 94, 104, 94, 107, 112, 108, 108, 109, 109, 121, 108, 108, 120, 122, 122, 128, 130, 122, 140, 122, 122, 140, 122, 134, 141, 136, 136, 154, 155, 155, 150, 161, 162, 169, 171, 181, 175, 175, 163, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178];
let mut kalman = Kalman2D::new(dt, ux, uy, std_dev_a, std_dev_mx, std_dev_my);
// Assume that initial X,Y coordinates match the first measurement
kalman.x.x = xs[0] as f32;
kalman.x.y = ys[0] as f32;
let mut predictions: Vec
## 2-D Kalman filter
Considering acceleration motion again let's write down its equations:
Considering the same physical model as in $(13)$ - $(14)$ let's write down state vector $\chi_{k}$:
$$\chi_{k} = \begin{bmatrix}
x_{k} \\
y_{k} \\
x'_ {k} \\
y'_ {k} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}
x_{k-1} + x'_ {k-1}\Delta t + \frac{x''_ {k-1}(\Delta t^2)}{2} \\
y_{k-1} + y'_ {k-1}\Delta t + \frac{y''_ {k-1}(\Delta t^2)}{2} \\
x'_ {k-1} + x''_ {k-1}\Delta t \\
y'_ {k-1} + y''_ {k-1}\Delta t
\end{bmatrix} \tag{27}$$
Matrix form of $\chi_{k}$ :
$$\chi_{k} = \begin{bmatrix} x_{k} \\
y_{k} \\
x'_ {k} \\
y'_ {k}
\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & \Delta t & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 0 & \Delta t \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} ⋅ \begin{bmatrix} x_{k-1} \\
y_{k-1} \\
x'_ {k-1} \\
y'_ {k-1} \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} & 0 \\
0 & \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \\
\Delta t & 0 \\
0 & \Delta t \end{bmatrix} ⋅ \begin{bmatrix} x''_ {k-1} \\
y''_ {k-1} \end{bmatrix} = $$
$$ = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & \Delta t & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 0 & \Delta t \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} ⋅ \chi_{k-1} + \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} & 0 \\
0 & \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \\
\Delta t & 0 \\
0 & \Delta t \end{bmatrix} ⋅ \begin{bmatrix} x''_ {k-1} \\
y''_{k-1} \end{bmatrix} \tag{28}$$
$$ \text{Assuming that $x''$ and $y''$ - is acceleration $a$, }$$
$$ a_{k-1} = \begin{bmatrix} x''_ {k-1} \\
y''_{k-1} \end{bmatrix} \tag{29}$$
$$\chi_{k} = \begin{bmatrix} x_{k} \\
y_{k} \\
x'_ {k} \\
y'_ {k}
\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & \Delta t & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 0 & \Delta t \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} ⋅ \chi_{k-1} + \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} & 0 \\
0 & \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \\
\Delta t & 0 \\
0 & \Delta t \end{bmatrix} ⋅ a_{k-1} \tag{30}$$
Taking close look on $(16)$ and $(1)$ we can write transition matrix $A$ and control input matrix $B$ as follows:
$$A = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & \Delta t & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 0 & \Delta t \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \tag{31}$$
$$B = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} & 0 \\
0 & \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \\
\Delta t & 0 \\
0 & \Delta t \end{bmatrix} \tag{32}$$
Let's find transformation matrix $H$. According to $(2)$ and $(19)$ - $(20)$:
$$z_{k} = H⋅\chi_{k} + v_{k} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} ⋅\begin{bmatrix} x_{k} \\
y_{k} \\
{x'_ {k}} \\
{y'_ {k}} \end{bmatrix} + v_{k} \tag{33}$$
$$ H = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \tag{34}$$
Process noise covariance matrix $Q$:
$$Q = \begin{matrix}
& \begin{matrix}x && y && x' && y'\end{matrix} \\
\begin{matrix}x \\
y \\
x' \\
y'\end{matrix} &
\begin{bmatrix} \sigma^2_{x} & 0 & \sigma_{x} \sigma_{x'} & 0 \\
0 & \sigma^2_{y} & 0 & \sigma_{y} \sigma_{y'} \\
\sigma_{x'} \sigma_{x} & 0 & \sigma^2_{x'} & 0 \\
0 & \sigma_{y'} \sigma_{y} & 0 & \sigma^2_{y'}\end{bmatrix}
\\\\
\end{matrix} \tag{35}$$
$$\text{, where} $$
$$ \text{$\sigma_{x}$ - standart deviation of position for $x$ component} $$
$$ \text{$\sigma_{y}$ - standart deviation of position for $y$ component} $$
$$ \text{$\sigma_{x'}$ - standart deviation of velocity for $x$ component} $$
$$ \text{$\sigma_{y'}$ - standart deviation of velocity for $y$ component} $$
Since we know about $(14)$ we can define $\sigma_{x}$, $\sigma_{y}$, $\sigma_{x'}$ and $\sigma_{y'}$ as:
$$ \sigma_{x} = \sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \tag{36}$$
$$ \sigma_{y} = \sigma_{y''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \tag{37}$$
$$ \sigma_{x'} = \sigma_{x''} \Delta t \tag{38}$$
$$ \sigma_{y'} = \sigma_{y''} \Delta t \tag{39}$$
$$\text{, where $\sigma_{x''}$ and $\sigma_{y''}$ - standart deviation of acceleration (tuned values)} $$
And now process noise covariance matrix $Q$ could be defined as:
$$ Q = \begin{bmatrix} (\sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & 0 & \sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \sigma_{x''} \Delta t & 0 \\
0 & (\sigma_{y''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & 0 & \sigma_{y''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \sigma_{y''} \Delta t \\
\sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \sigma_{x''} \Delta t & 0 & (\sigma_{x''} \Delta t)^2 & 0 \\
0 & \sigma_{y''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \sigma_{y''} \Delta t & 0 & (\sigma_{y''} \Delta t)^2 \end{bmatrix} = $$
$$ = \begin{bmatrix} (\sigma_{x''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & 0 & (\sigma_{x''})^2 \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \Delta t & 0 \\
0 & (\sigma_{y''} \frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & 0 & (\sigma_{y''})^2 \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \Delta t \\
(\sigma_{x''})^2 \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \Delta t & 0 & (\sigma_{x''} \Delta t)^2 & 0 \\
0 & (\sigma_{y''})^2 \frac{\Delta t^2}{2}\Delta t & 0 & (\sigma_{y''} \Delta t)^2 \end{bmatrix} = \text{| Knowing that $x''$ and $y''$ - acceleration|} = $$
$$ = \begin{bmatrix} (\frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & 0 & \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \Delta t & 0 \\
0 & (\frac{\Delta t^2}{2})^2 & 0 & \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \Delta t \\
\frac{\Delta t^2}{2} \Delta t & 0 & \Delta t^2 & 0 \\
0 & \Delta t \frac{\Delta t^2}{2} & 0 & \Delta t^2 \end{bmatrix} \sigma^2_{a''}$$
$$ = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\Delta t^4}{4} & 0 & \frac{\Delta t^3}{2} & 0 \\
0 & \frac{\Delta t^4}{4} & 0 & \frac{\Delta t^3}{2} \\
\frac{\Delta t^3}{2} & 0 & \Delta t^2 & 0 \\
0 & \frac{\Delta t^3}{2} & 0 & \Delta t^2 \end{bmatrix} \sigma^2_{a''} \tag{40}$$
Covariance of measurement noise $R$ is matrix of size $2 \times 2$ (since there are two components - $x$ and $y$) and it is defined as variance of the measurement noise:
$$R = \begin{matrix}
\begin{matrix}& x & y\end{matrix} \\
\begin{matrix}x \\
y \end{matrix}
\begin{bmatrix}\sigma^2_{x} & 0 \\
0 & \sigma^2_{y} \end{bmatrix}
\\\\
\end{matrix} = \begin{bmatrix}\sigma^2_{x} & 0 \\
0 & \sigma^2_{y} \end{bmatrix} \tag{41}$$
Rust implementation is [here](./src/kalman/kalman_2d.rs#L4)
Example of usage:
```rust
let dt = 0.04; // 1/25 = 25 fps - just an example
let ux = 1.0;
let uy = 1.0;
let std_dev_a = 2.0;
let std_dev_mx = 0.1;
let std_dev_my = 0.1;
// Sample measurements
// Note: in this example Y-axis going from up to down
let xs = vec![311, 312, 313, 311, 311, 312, 312, 313, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 311, 311, 311, 311, 311, 310, 311, 311, 311, 310, 310, 308, 307, 308, 308, 308, 307, 307, 307, 308, 307, 307, 307, 307, 307, 308, 307, 309, 306, 307, 306, 307, 308, 306, 306, 306, 305, 307, 307, 307, 306, 306, 306, 307, 307, 308, 307, 307, 308, 307, 306, 308, 309, 309, 309, 309, 308, 309, 309, 309, 308, 311, 311, 307, 311, 307, 313, 311, 307, 311, 311, 306, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312];
let ys = vec![5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 12, 12, 13, 16, 16, 18, 18, 19, 19, 20, 20, 22, 22, 23, 23, 24, 24, 28, 30, 32, 35, 39, 42, 44, 46, 56, 58, 70, 60, 52, 64, 51, 70, 70, 70, 66, 83, 80, 85, 80, 98, 79, 98, 61, 94, 101, 94, 104, 94, 107, 112, 108, 108, 109, 109, 121, 108, 108, 120, 122, 122, 128, 130, 122, 140, 122, 122, 140, 122, 134, 141, 136, 136, 154, 155, 155, 150, 161, 162, 169, 171, 181, 175, 175, 163, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178];
let mut kalman = Kalman2D::new(dt, ux, uy, std_dev_a, std_dev_mx, std_dev_my);
// Assume that initial X,Y coordinates match the first measurement
kalman.x.x = xs[0] as f32;
kalman.x.y = ys[0] as f32;
let mut predictions: Vec ## 2-D Kalman filter (with acceleration component and no control input)
__W.I.P.__
@todo: math-jax / rust code / rust test / plots
## How to use
Add dependency to your Cargo.toml file
```toml
[package]
....
[dependencies]
...
kalman-rust = "0.2.2"
...
```
Start using it, e.g. Kalman2D:
```rust
use kalman_rust::kalman::{
Kalman2D
};
fn main() {
let dt = 0.04; // 1/25 = 25 fps - just an example
let ux = 1.0;
let uy = 1.0;
let std_dev_a = 2.0;
let std_dev_mx = 0.1;
let std_dev_my = 0.1;
// Sample measurements
// Note: in this example Y-axis going from up to down
let xs = vec![311, 312, 313, 311, 311, 312, 312, 313, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 311, 311, 311, 311, 311, 310, 311, 311, 311, 310, 310, 308, 307, 308, 308, 308, 307, 307, 307, 308, 307, 307, 307, 307, 307, 308, 307, 309, 306, 307, 306, 307, 308, 306, 306, 306, 305, 307, 307, 307, 306, 306, 306, 307, 307, 308, 307, 307, 308, 307, 306, 308, 309, 309, 309, 309, 308, 309, 309, 309, 308, 311, 311, 307, 311, 307, 313, 311, 307, 311, 311, 306, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312];
let ys = vec![5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 12, 12, 13, 16, 16, 18, 18, 19, 19, 20, 20, 22, 22, 23, 23, 24, 24, 28, 30, 32, 35, 39, 42, 44, 46, 56, 58, 70, 60, 52, 64, 51, 70, 70, 70, 66, 83, 80, 85, 80, 98, 79, 98, 61, 94, 101, 94, 104, 94, 107, 112, 108, 108, 109, 109, 121, 108, 108, 120, 122, 122, 128, 130, 122, 140, 122, 122, 140, 122, 134, 141, 136, 136, 154, 155, 155, 150, 161, 162, 169, 171, 181, 175, 175, 163, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178];
// Assume that initial X,Y coordinates match the first measurement
let ix = xs[0] as f32; // Initial state for X
let iy = ys[0] as f32; // Initial state for Y
let mut kalman = Kalman2D::new_with_state(dt, ux, uy, std_dev_a, std_dev_mx, std_dev_my, ix, iy);
let mut predictions: Vec
## 2-D Kalman filter (with acceleration component and no control input)
__W.I.P.__
@todo: math-jax / rust code / rust test / plots
## How to use
Add dependency to your Cargo.toml file
```toml
[package]
....
[dependencies]
...
kalman-rust = "0.2.2"
...
```
Start using it, e.g. Kalman2D:
```rust
use kalman_rust::kalman::{
Kalman2D
};
fn main() {
let dt = 0.04; // 1/25 = 25 fps - just an example
let ux = 1.0;
let uy = 1.0;
let std_dev_a = 2.0;
let std_dev_mx = 0.1;
let std_dev_my = 0.1;
// Sample measurements
// Note: in this example Y-axis going from up to down
let xs = vec![311, 312, 313, 311, 311, 312, 312, 313, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 311, 311, 311, 311, 311, 310, 311, 311, 311, 310, 310, 308, 307, 308, 308, 308, 307, 307, 307, 308, 307, 307, 307, 307, 307, 308, 307, 309, 306, 307, 306, 307, 308, 306, 306, 306, 305, 307, 307, 307, 306, 306, 306, 307, 307, 308, 307, 307, 308, 307, 306, 308, 309, 309, 309, 309, 308, 309, 309, 309, 308, 311, 311, 307, 311, 307, 313, 311, 307, 311, 311, 306, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312, 312];
let ys = vec![5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 12, 12, 13, 16, 16, 18, 18, 19, 19, 20, 20, 22, 22, 23, 23, 24, 24, 28, 30, 32, 35, 39, 42, 44, 46, 56, 58, 70, 60, 52, 64, 51, 70, 70, 70, 66, 83, 80, 85, 80, 98, 79, 98, 61, 94, 101, 94, 104, 94, 107, 112, 108, 108, 109, 109, 121, 108, 108, 120, 122, 122, 128, 130, 122, 140, 122, 122, 140, 122, 134, 141, 136, 136, 154, 155, 155, 150, 161, 162, 169, 171, 181, 175, 175, 163, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178, 178];
// Assume that initial X,Y coordinates match the first measurement
let ix = xs[0] as f32; // Initial state for X
let iy = ys[0] as f32; // Initial state for Y
let mut kalman = Kalman2D::new_with_state(dt, ux, uy, std_dev_a, std_dev_mx, std_dev_my, ix, iy);
let mut predictions: Vec