basegeom
| Crates.io | basegeom |
| lib.rs | basegeom |
| version | 0.3.11 |
| created_at | 2025-08-10 06:26:56.85389+00 |
| updated_at | 2025-08-23 10:48:22.314287+00 |
| description | A library for 2D geometry, providing geometric algorithms for intersection/distance between circular arcs/line segments. |
| homepage | |
| repository | https://github.com/radevgit/basegeom |
| max_upload_size | |
| id | 1788590 |
| size | 560,049 |
documentation
README
BaseGeom
Adding the library to Cargo.toml
[dependencies]
basegeom = "0.3.11"
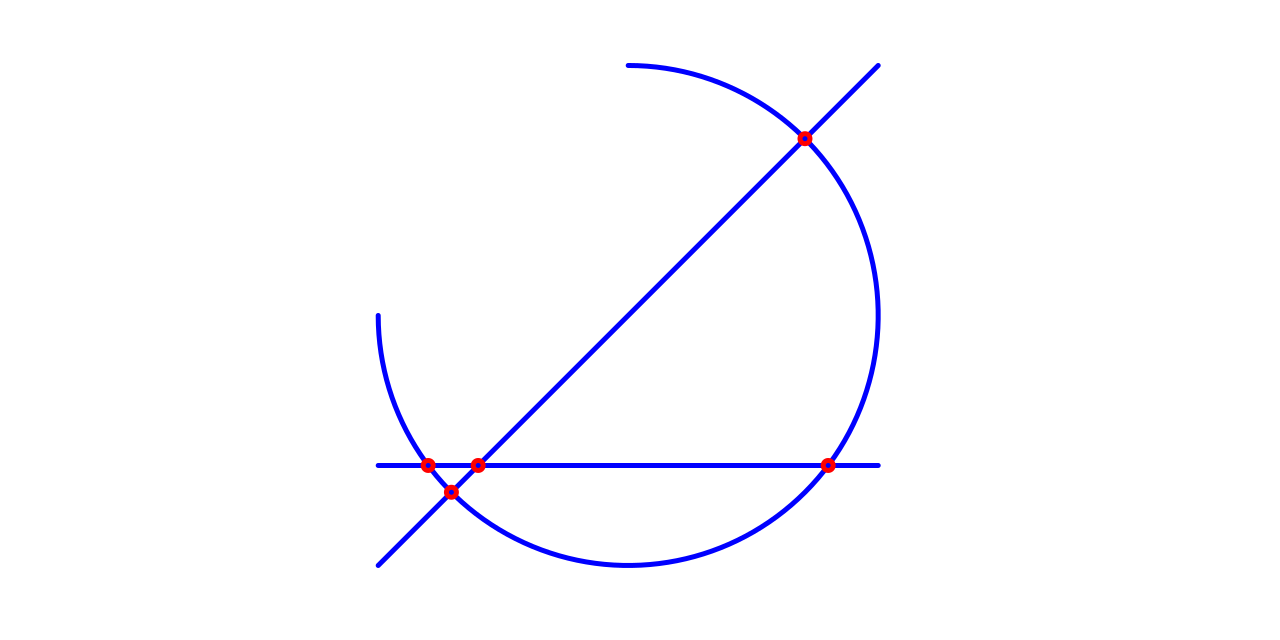
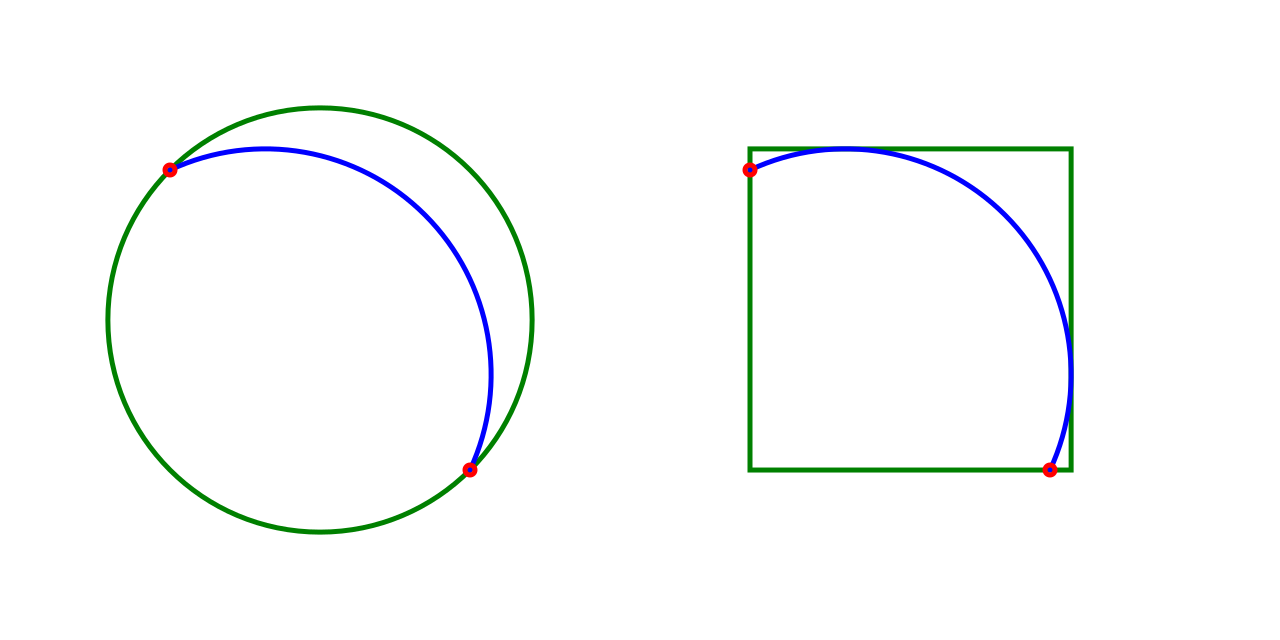
Documentation
Basic 2D geometric operations
The intention of this library is to provide a 2D geometric operations for arcs and line segments. It is intended for use in My other projects, and may not implement all possible geometric operations.
Implemented Features
- Point creation and manipulation
- Line segments and circle arcs
- Distance calculations between points, line segments, and circle arcs
- Intersection tests for various geometric primitives
- Arc representation and manipulation
- Support for polylines and vertex manipulation
Distance Functions
- dist_arc_arc
- dist_line_circle
- dist_point_arc
- dist_point_circle
- dist_point_segment
- dist_segment_arc
- dist_segment_circle
- dist_segment_segment
Intersection Functions
- int_arc_arc
- int_circle_circle
- int_interval_interval
- int_line_arc
- int_line_circle
- int_line_line
- int_segment_arc
- int_segment_circle
- int_segment_segment
- if_really_intersecting_arc_arc
- if_really_intersecting_segment_arc
- if_really_intersecting_segment_segment
Geometric Primitives
- Points
- Line Segments
- Circles
- Circle Arcs
- Polylines
- Intervals
- PVertices (point, bulge)
Point (vector) Manipulation
- add, sub, neg, mul(f64), div(f64)
- dot
- perp
- norm
- normalize
- almost_eq (ULP-s)
- close_enough (eps)
- lerp
- sort_colinear_points
Utilities functions
- almost_equal_as_int (ULP-s)
- perturbed_ulps_as_int (ULP-s)
- close_enough (eps)
- diff_of_prod
- sum_of_prod
Algorithms
- Convex Hull (Pointline)
- Convexity Detection (Pointline)
- Area Calculations (Pointline and Arcline)
- Bounding Circle (Arc)
- Bounding Rectangle (Arc)
Examples
Creating and working with points (vectors)
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Create points using the constructor or convenience function
let p1 = Point::new(1.0, 2.0);
let p2 = point(3.0, 4.0);
// Points support arithmetic operations
let sum = p1 + p2;
assert_eq!(sum.x, 4.0);
assert_eq!(sum.y, 6.0);
// Calculate distance between points
let distance = (p2 - p1).norm();
assert!((distance - 2.828427124746190).abs() < 1e-10);
Working with geometric primitives
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Create a circle and segment
let center = point(0.0, 0.0);
let c = circle(center, 5.0);
let seg = segment(point(-3.0, 0.0), point(3.0, 0.0));
assert_eq!(c.c, center); // Circle center field is 'c'
assert_eq!(c.r, 5.0); // Circle radius field is 'r'
assert_eq!(seg.a.x, -3.0);
assert_eq!(seg.b.x, 3.0);
Distance computations
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Distance from point to circle returns (distance, closest_point, is_equidistant)
let p = point(10.0, 0.0);
let c = circle(point(0.0, 0.0), 5.0);
let (dist, closest, _is_equidistant) = dist_point_circle(&p, &c);
assert_eq!(dist, 5.0);
// Distance from point to segment returns (distance, closest_point)
let seg = segment(point(0.0, 0.0), point(5.0, 0.0));
let p = point(2.5, 3.0);
let (dist, _closest) = dist_point_segment(&p, &seg);
assert_eq!(dist, 3.0);
Intersection computations
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Test intersection between two circles
let c1 = circle(point(0.0, 0.0), 3.0);
let c2 = circle(point(4.0, 0.0), 3.0);
let result = int_circle_circle(c1, c2);
// Two circles with overlapping areas should intersect at two points
match result {
CircleCircleConfig::NoncocircularTwoPoints(_, _) => {
// Two intersection points found
assert!(true);
},
_ => {
// No intersection or other cases
assert!(false);
}
}
Working with arcs
[!IMPORTANT] Arcs are always CCW (counter-clockwise) in this library.
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Create an arc from three points and radius (start, end, center, radius)
let start = point(1.0, 0.0);
let end = point(0.0, 1.0);
let center = point(0.0, 0.0);
let a = arc(start, end, center, 1.0);
assert_eq!(a.a, start); // Arc start point field is 'a'
assert_eq!(a.b, end); // Arc end point field is 'b'
assert_eq!(a.c, center); // Arc center field is 'c'
assert_eq!(a.r, 1.0); // Arc radius field is 'r'
Working with lines
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Create a line from a point and direction vector
let origin = point(0.0, 0.0);
let direction = point(1.0, 1.0);
let l = line(origin, direction);
assert_eq!(l.origin, origin);
assert_eq!(l.dir, direction);
Working with intervals
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Create an interval (tuple struct with two f64 values)
let iv = interval(1.0, 5.0);
assert_eq!(iv.0, 1.0); // First endpoint
assert_eq!(iv.1, 5.0); // Second endpoint
// Test if a value is contained in the interval
assert!(iv.contains(3.0));
assert!(!iv.contains(6.0));
Working with polylines (PVertex)
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Create vertices for a polyline
let p1 = pvertex(point(0.0, 0.0), 0.0);
let p2 = pvertex(point(1.0, 0.0), 0.0);
let p3 = pvertex(point(1.0, 1.0), 0.0);
let polyline = vec![p1, p2, p3];
// Translate the polyline (returns a new polyline)
let offset = point(2.0, 3.0);
let translated = polyline_translate(&polyline, offset);
assert_eq!(translated[0].p.x, 2.0);
assert_eq!(translated[0].p.y, 3.0);
Arc-arc distance computation
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Create two separate arcs
let a1 = arc(point(1.0, 0.0), point(-1.0, 0.0), point(0.0, 0.0), 1.0);
let a2 = arc(point(4.0, 0.0), point(2.0, 0.0), point(3.0, 0.0), 1.0);
// Compute distance between arcs (returns just the distance as f64)
let dist = dist_arc_arc(&a1, &a2);
assert_eq!(dist, 1.0); // Distance between the arc edges
Line-circle intersection
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Create a line and circle that intersect
let l = line(point(-3.0, 0.0), point(1.0, 0.0)); // Horizontal line through origin
let c = circle(point(0.0, 0.0), 2.0);
let result = int_line_circle(&l, &c);
match result {
LineCircleConfig::TwoPoints(..) => {
// Line intersects circle at two points
assert!(true);
},
_ => assert!(false),
}
Segment-segment intersection
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Create two intersecting segments
let seg1 = segment(point(0.0, 0.0), point(2.0, 2.0));
let seg2 = segment(point(0.0, 2.0), point(2.0, 0.0));
let result = int_segment_segment(&seg1, &seg2);
match result {
SegmentSegmentConfig::OnePoint(pt, ..) => {
// Segments intersect at one point (should be around (1,1))
assert!(point(1.0, 1.0).close_enough(pt, 1e-10));
},
_ => assert!(false),
}
Utility functions
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Test floating point equality with tolerance
assert!(close_enough(1.0, 1.0000001, 1e-5));
assert!(!close_enough(1.0, 1.1, 1e-5));
// Check if two floats are almost equal using integer comparison
assert!(almost_equal_as_int(1.0, 1.0, 0));
Arc-Arc intersection
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Create two intersecting arcs
let a1 = arc(point(1.0, 0.0), point(0.0, 1.0), point(0.0, 0.0), 1.0);
let a2 = arc(point(1.0, 1.0), point(0.0, 0.0), point(1.0, 0.0), 1.0);
let result = int_arc_arc(&a1, &a2);
match result {
ArcArcConfig::NonCocircularOnePoint(pt) => {
// Arcs intersect at one point
assert_eq!(point(0.5, 0.8660254037844386), pt);
},
_ => {
// Could be two points, no intersection, or other cases
assert!(false); // Accept other valid intersection results
}
}
Distance computations
use basegeom::prelude::*;
let l = line(point(0.0, 3.0), point(1.0, 0.0)); // Line with point and direction
let c = circle(point(0.0, 0.0), 2.0);
let result = dist_line_circle(&l, &c);
match result {
DistLineCircleConfig::OnePair(dist, _param, _line_pt, _circle_pt) => {
assert_eq!(1.0, dist);
}
_ => assert!(false), // Accept other valid distance results
}
// Distance from point to arc
let p = point(2.0, 0.0);
let a = arc(point(0.0, 1.0), point(1.0, 0.0), point(0.0, 0.0), 1.0);
match dist_point_arc(&p, &a) {
DistPointArcConfig::OnePoint(dist, _) => {
assert_eq!(1.0, dist);
}
_ => assert!(false), // Accept other valid distance results
}
// Distance from segment to arc
let seg = segment(point(3.0, 0.0), point(4.0, 0.0));
let a = arc(point(0.0, 1.0), point(1.0, 0.0), point(0.0, 0.0), 1.0);
let dist = dist_segment_arc(&seg, &a);
assert_eq!(2.0, dist);
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Distance from segment to circle
let seg = segment(point(3.0, 0.0), point(4.0, 0.0));
let c = circle(point(0.0, 0.0), 1.0);
let result = dist_segment_circle(&seg, &c);
// Function returns DistSegmentCircleConfig enum
match result {
DistSegmentCircleConfig::OnePoint(dist, closest) => {
assert_eq!(2.0, dist); // Distance should be non-negative
}
_ => assert!(false), // Accept any valid distance result
}
// Distance between two segments
let seg1 = segment(point(0.0, 0.0), point(1.0, 0.0));
let seg2 = segment(point(0.0, 2.0), point(1.0, 2.0));
let dist = dist_segment_segment(&seg1, &seg2);
assert_eq!(dist, 2.0); // Parallel segments 2 units apart
Intersection computations
use basegeom::prelude::*;
let seg1 = segment(point(0.0, 0.0), point(1.0, 0.0));
let seg2 = segment(point(0.0, 2.0), point(1.0, 2.0));
let dist = dist_segment_segment(&seg1, &seg2);
assert_eq!(dist, 2.0); // Parallel segments 2 units apart
Intersection computations
use basegeom::prelude::*;
// Interval-interval intersection
let iv1 = interval(1.0, 5.0);
let iv2 = interval(3.0, 7.0);
let result = int_interval_interval(iv1, iv2);
match result {
IntervalConfig::Overlap(start, end) => {
// Intervals overlap from 3.0 to 5.0
assert_eq!(start, 3.0);
assert_eq!(end, 5.0);
},
_ => assert!(false), // Accept other valid intersection results
}
// Line-line intersection
let l1 = line(point(0.0, 0.0), point(1.0, 0.0)); // Line with origin and direction
let l2 = line(point(0.0, 0.0), point(0.0, 1.0)); // Line with origin and direction
let result = int_line_line(&l1, &l2);
match result {
LineLineConfig::OnePoint(pt, _param1, _param2) => {
// Lines intersect at origin
assert_eq!(point(0.0, 0.0), pt);
},
_ => assert!(false), // Accept other valid intersection results
}
Area Calculations
use basegeom::prelude::*;
use basegeom::algo::{pointline_area, arcline_area};
// Calculate area of a polygon defined by points
let triangle = vec![
point(0.0, 0.0),
point(4.0, 0.0),
point(2.0, 3.0),
point(0.0, 0.0) // Close the polygon
];
let area = pointline_area(&triangle);
assert_eq!(area, 6.0); // Triangle area = 0.5 * base * height = 0.5 * 4 * 3 = 6
// Calculate area of a shape with both line segments and arcs
let square_with_arc = vec![
arc(point(0.0, 0.0), point(2.0, 0.0), point(0.0, 0.0), 0.0), // Bottom edge (line)
arc(point(2.0, 0.0), point(2.0, 2.0), point(0.0, 0.0), 0.0), // Right edge (line)
arc(point(2.0, 2.0), point(0.0, 2.0), point(1.0, 3.0), 1.0), // Top edge (semicircle)
arc(point(0.0, 2.0), point(0.0, 0.0), point(0.0, 0.0), 0.0), // Left edge (line)
];
let area_with_arc = arcline_area(&square_with_arc);
// Area includes the square plus the semicircular bulge
assert_eq!(area_with_arc, 5.356194490192345);
Bounding Calculations
use basegeom::prelude::*;
use basegeom::algo::{arc_bounding_circle, arc_bounding_rect};
// Find the smallest circle that contains an arc
let quarter_arc = arc(point(1.0, 0.0), point(0.0, 1.0), point(0.0, 0.0), 1.0);
let bounding_circle = arc_bounding_circle(&quarter_arc);
// For a quarter circle, the bounding circle is smaller than the arc's own circle
assert_eq!(bounding_circle.r, 0.7071067811865476); // sqrt(2)/2
// Find the smallest axis-aligned rectangle that contains an arc
let semicircle = arc(point(-1.0, 0.0), point(1.0, 0.0), point(0.0, 0.0), 1.0);
let bounding_rect = arc_bounding_rect(&semicircle);
// Rectangle should span from -1 to 1 in x, and include the arc's extremes
assert_eq!(bounding_rect.p1.x, -1.0); // min_x
assert_eq!(bounding_rect.p2.x, 1.0); // max_x
// Bounding rectangle for a line segment
let line_segment = arcseg(point(1.0, 2.0), point(4.0, 6.0));
let line_rect = arc_bounding_rect(&line_segment);
assert_eq!(line_rect.p1, point(1.0, 2.0)); // Bottom-left corner
assert_eq!(line_rect.p2, point(4.0, 6.0)); // Top-right corner
Convex Hull Computation
use basegeom::prelude::*;
use basegeom::algo::{pointline_convex_hull, is_convex_pointline};
// Find the convex hull of a set of points
let points = vec![
point(0.0, 0.0),
point(2.0, 1.0),
point(1.0, 2.0), // Interior point (will be excluded)
point(3.0, 0.0),
point(2.0, 3.0),
point(0.0, 2.0),
];
let hull = pointline_convex_hull(&points);
// Hull should contain only the exterior points
assert_eq!(hull.len(), 4); // 4 points on the convex hull
// Check if a polygon is convex
let convex_polygon = vec![
point(0.0, 0.0),
point(2.0, 0.0),
point(2.0, 2.0),
point(0.0, 2.0),
];
assert!(is_convex_pointline(&convex_polygon)); // Square is convex
let concave_polygon = vec![
point(0.0, 0.0),
point(2.0, 0.0),
point(2.0, 2.0),
point(1.0, 1.0), // Creates concave indentation
point(0.0, 2.0),
];
assert!(!is_convex_pointline(&concave_polygon)); // This shape is concave