cubipods
| Crates.io | cubipods |
| lib.rs | cubipods |
| version | 0.1.1 |
| created_at | 2024-08-26 17:46:02.826042+00 |
| updated_at | 2024-09-10 22:59:48.847247+00 |
| description | A minimal EVM implemented in Rust. |
| homepage | |
| repository | |
| max_upload_size | |
| id | 1352471 |
| size | 195,428 |
documentation
README
Cubipods
Cubipods is a minimal Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) written in Rust. This project offers a lightweight and efficient platform for running EVM bytecode, complete with features like lexical analysis, stack management, memory handling, and storage operations. Cubipods can execute bytecode consisting of EVM opcodes and provides detailed output for stack, memory, and storage states after execution.
Features
- Lexical Analysis: Tokenizes bytecode and analyzes the included opcodes.
- Stack Management: Supports standard stack operations, enabling proper opcode execution.
- Memory Handling: Implements memory operations to replicate EVM behavior.
- Storage Operations: Manages storage functionalities as per EVM standards.
- Bytecode Execution: Runs user-provided bytecode, processing EVM opcodes.
- Verbose Output: Provides detailed output, including execution history and the final state of the stack, memory, and storage.
Basics
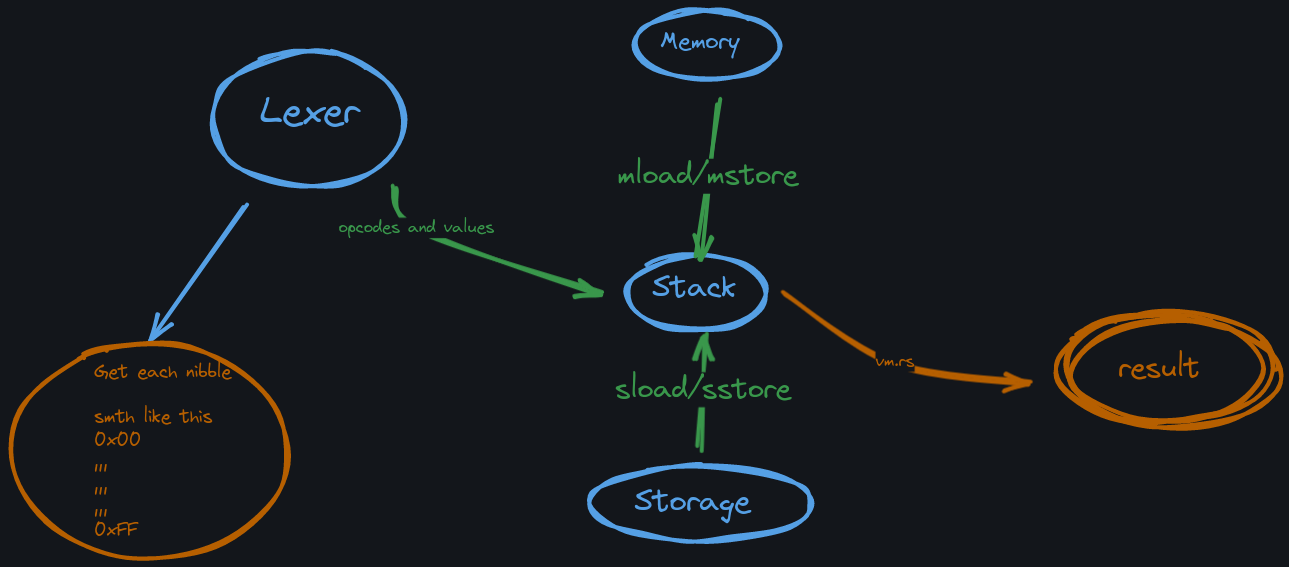
Supported Instructions
Cubipods currently supports the following EVM opcodes:
STOP(0x00)ADD(0x01)MUL(0x02)SUB(0x03)DIV(0x04)MOD(0x06)EXP(0x0a)LT(0x10)GT(0x11)EQ(0x14)ISZERO(0x15)AND(0x16)OR(0x17)XOR(0x18)NOT(0x19)BYTE(0x1a)KECCAK256(0x20)POP(0x50)MLOAD(0x51)MSTORE(0x52)SLOAD(0x54)SSTORE(0x55)PUSH0toPUSH32DUP1toDUP16SWAP1toSWAP16
Usage
Cubipods can be used through its command-line interface (CLI). Users can provide bytecode for execution and optionally enable verbose mode to get detailed output.
Installation
You can add Cubipods to your project using Cargo. Run the following command:
cargo install cubipods
Command Line Interface
Here are the available CLI options:
-b, --bytecode <BYTECODE>: Bytecode consisting of EVM opcodes to be executed.-v, --verbose: Enables verbose mode, printing execution history and final states of Stack, Memory, and Storage.
Examples
Execute a bytecode:
cubipods -b 6003600201
- The example above pushes the values
0x03and0x02onto the stack and then adds them together (PUSH1 0x03,PUSH1 0x02,ADD).
Enable verbose mode:
cubipods -b 6003600201 -v
Contributing
To contribute to Cubipods, follow these steps:
- Fork the repository.
- Create a new branch for your feature or bugfix.
- Make your changes.
- Test thoroughly.
- Submit a pull request.
Code Structure
- main.rs: Entry point of the application.
- cli.rs: Command-line interface definition and argument parsing.
- bytecode.rs: Handles bytecode parsing and execution.
- stack.rs: Manages stack operations and state.
- memory.rs: Implements memory functionalities.
- storage.rs: Handles storage operations.
License
Cubipods is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for more details.
Acknowledgements
This project uses the following crates:
clapfor command-line argument parsing.tiny-keccakfor cryptographic hashing functions.hexfor hexadecimal encoding and decoding.
Thank you for using Cubipods! If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to open an issue on GitHub. Happy coding!