deser-incomplete
| Crates.io | deser-incomplete |
| lib.rs | deser-incomplete |
| version | 0.1.2 |
| created_at | 2025-02-09 23:36:57.006311+00 |
| updated_at | 2025-03-25 01:30:58.28172+00 |
| description | Deserialize incomplete or broken data with Serde |
| homepage | |
| repository | https://github.com/bgeron/deser-incomplete/ |
| max_upload_size | |
| id | 1549426 |
| size | 812,687 |
documentation
README
deser-incomplete: Deserialize incomplete or broken data with Serde
Parse incomplete or broken data with existing Serde data formats.
This is nice for ingesting streaming JSON, which is technically invalid until the stream is done. By tolerating premature end of input, we can immediately make use of the streaming input.

Here, we wrapped serde_json with deser-incomplete, and printed the Rust
debug representation of the result. We also reserialized to JSON and
let nushell do its beautiful table formatting.
The JSON can also come from an external program. Here is a demo program that computes disk usage of directories and outputs the results as JSON. In true Unix style, displaying for the user is a separate concern, implemented by a separate program.

deser-incomplete sits between #[serde(Deserialize)] and the data format. When a parse
error is detected (presumably because the input ended), it safely halts parsing.
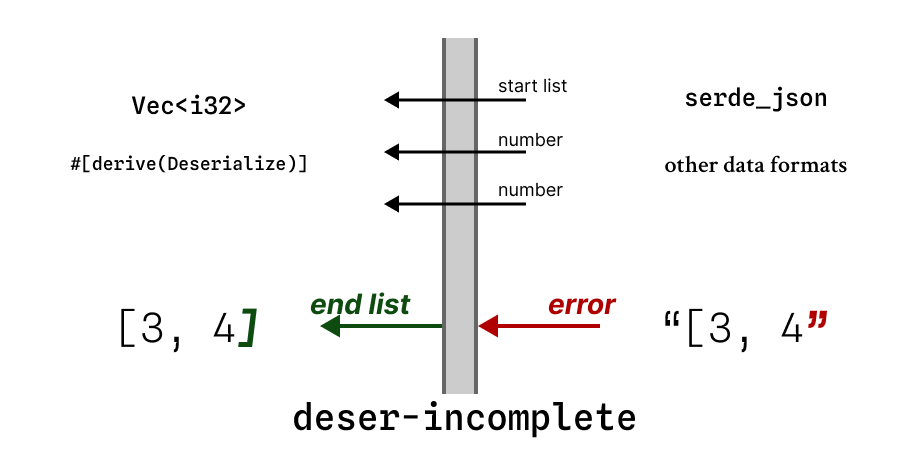
How to use: JSON and YAML
let result: Result<Vec<u32>, deser_incomplete::Error<serde_json::Error>>
= deser_incomplete::from_json_str("[3, 4, ");
assert_eq!(result.unwrap(), vec![3, 4]);
let result: Result<Vec<bool>, deser_incomplete::Error<serde_yaml::Error>>
= deser_incomplete::from_yaml_str("- true\n- false\n- ");
assert_eq!(result.unwrap(), vec![true, false]);
Command line:
$ cargo install deser-incomplete --example repair-deser
$ echo '[3, 4' | repair-deser # JSON by default
[3,4]
How to use: other data formats
-
You need to explain how to create the
Deserializerby implementingSource.- If your format has
&mut T: Deserializerthen mimicsource::JsonStr. - If your format has
T: Deserializerthen mimicsource::YamlStr.
- If your format has
-
Some formats need a trailer for best results. For example,
from_json_strappends a double-quote to the input before parsing, this letsserde_jsonsee strings that weren't actually complete.We also preprocess the input in
from_yaml_str, actually there it is even more important for good results.Add preprocessing with
Options::set_random_trailer, or turn it off such preprocessing withOptions::disable_random_tag. You can see the effect of it withcargo run --example live -- --use-random-trailer false.I expect that binary formats don't need this preprocessing.
How this works internally
The implementation sits in between Deserialize, Deserializer, and Visitor,
gathers metadata during the parse, and saves successful sub-parses. It also "backtracks":
if a parse fails, then we retry, but just before the failure point we swap out the real
Deserializer for a decoy which can brings deserialization to a safe end.
We apply multiple techniques. Suppose we want to parse Vec<u32> with serde_json.
Here are the main techniques.
-
(Example: parse empty JSON as
[].) — On the top level, if parsing fails immediately (e.g. empty input) but a sequence is expected, then return[].[setting name: fallback_seq_empty_at_root]
-
(Example: parse JSON
"[3"as[3].) — When there are no more elements in a sequence, let theVisitorconstruct theVec<u32>and put it somewhere safe. Nowserde_json::Deserializer::deserialize_seqnotices the missing close bracket and returnsErrto us. We ignoreErr, retrieve the saved value again, and returnOkof it.This happens for every
deserialize_*method, not just sequences.[setting name: tolerate_deserializer_fail_after_visit_success]
-
(Example: parse JSON
"[3,"as[3].) — Inside a sequence, if parsing the next element will fail, then don't even try.This works using backtracking.
[setting name: backtrack_seq_skip_item]
-
Before deserializing, we append a random trailer.
Random trailer
Additionally we have a "random trailer" technique to get incomplete strings to parse. Unfortunately this technique is specific to the data format. This library implements it for JSON and YAML.
This technique is not applied by default for other data formats. Even with JSON/YAML, this
technique can be turned off with Options::disable_random_tag.
Random trailer for JSON
We actually append tRANDOM" to every JSON input, where RANDOM are some randomly chosen
letters. It turns out that serde_json can parse any prefix of valid JSON, as long
as we concatenate tRANDOM" to it. Some examples:
-
(Example:
"hello.) The concatenation is"hellotRANDOM"and we actually get this back fromserde_jsonthroughfn visit_borrowed_str--- afterserde_jsonremoved the double-quotes.In
fn visit_borrowed_str, we notice that the string ends inRANDOM. Because this is a random string of letters, it cannot have been part of the incomplete JSON input. We remove thetRANDOMsuffix and get back just"hello". -
(Example:
"hello\--- perhaps breaking in the middle of\n.) The concatenation is"hello\tRANDOM"; the\tparses to a tab character. We strip off<TAB>randomand again return"hello". -
(Example:
"hello".) The concatenation is"hello"tRANDOM". Nowserde_jsonvisits thehellostring as it would normally do, and if there should be any error after the visit, we can recover from it anyway as per tolerate_deserializer_fail_after_visit_success.
Inspecting at runtime
There is extensive logging through the tracing library, which becomes visible if you
initialize the library.
Guiding principles
The logic was hand-tweaked to the following criteria:
-
("soundness") For any complete and valid JSON/YAML, if you call
deser-incompleteon a prefix, then its output should not contain data that doesn't exist in the complete JSON/YAML. -
("monotone") A larger prefix should not parse to a shorter output.
-
("prompt") Ideally, each prefix contains as much data as we can be certain of.
The implementation of Deserializer (data format) may influence the quality of the output,
but the default ruleset does generally very well with serde_json and serde_yaml.
There are extensive snapshot tests that validate the quality of the output on these criteria.
If you are curious, then it is possible to tweak the ruleset
with unstable::UnstableCustomBehavior. We also have snapshot tests for some alternative
parsing configurations.
Notes and limitations
-
Ideally, your data format should be relatively greedy, in the sense that it generates information quickly and does not need to look ahead in the serialized stream too much.
-
This approach lets us safely abort parsing and get a value, but we cannot skip over invalid segments of input. (For that you need an approach like tree-sitter.)
-
We cannot distinguish eof from invalid input.
-
YAML works well in general, but it is a bit less exhaustively tested than JSON. The randomized trailer is really important for YAML.
-
JSON: when parsing a floating-point number, if the end of input happens to fall directly after the decimal point, then the number is missing from the output.
-
For YAML, the randomized trailer uses a heuristic to see if we are currently in an escape sequence in a string --- but this heuristic can fail. In this case, the incomplete string will be missing from the output.
Have fun!
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Annisa Chand and @XAMPPRocky for useful feedback.
License
Licensed under either of
- Apache License, Version 2.0, (LICENSE-APACHE or https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0)
- MIT license (LICENSE-MIT or https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
at your option.
Contribution
Unless you explicitly state otherwise, any contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the work by you, as defined in the Apache-2.0 license, shall be dual licensed as above, without any additional terms or conditions.
