math-core
| Crates.io | math-core |
| lib.rs | math-core |
| version | 0.2.2 |
| created_at | 2025-06-16 14:46:49.880056+00 |
| updated_at | 2026-01-10 11:08:46.312787+00 |
| description | Convert LaTeX equations to MathML Core |
| homepage | |
| repository | https://github.com/tmke8/math-core |
| max_upload_size | |
| id | 1714381 |
| size | 408,398 |
documentation
README
math-core – Convert LaTeX to MathML Core
math-core allows you to convert LaTeX math to MathML Core, the MathML specification that is being implemented by web browsers. For example, this LaTeX code:
\sum_{i=0}^N x_i
is converted to
<math display="block">
<munderover>
<mo lspace="0">∑</mo>
<mrow>
<mi>i</mi>
<mo lspace="0" rspace="0">=</mo>
<mn>0</mn>
</mrow>
<mi>N</mi>
</munderover>
<msub>
<mi>x</mi>
<mi>i</mi>
</msub>
</math>
which looks like this:
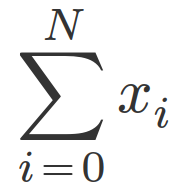
Goals
The goal of this project is to translate modern LaTeX math faithfully to the browser. More specifically, the goal is to…
- Support all common LaTeX math commands, at least those that KaTeX supports
- Produce concise, readable, and semantically correct MathML
- Try to avoid CSS hacks as much as possible (and definitely don’t use JavaScript in any way)
- Support many different math fonts
- Try to keep the compiled WebAssembly code small
This project is still in development, so not all LaTeX math commands that KaTeX supports are supported yet. See Development status below.
Usage
There are 4 ways to use the code in this project:
- As a CLI binary
- As a Python package
- As a Rust library
- As a WebAssembly module
CLI
You can download precompiled binaries from the GitHub Release page. Alternatively, you can build the CLI binary from source:
cargo build --bin mathcore --release
You can see an explanation of the CLI interface with
mathcore --help
A config file can be used to define custom LaTeX macros. An example of such a file is contained in this repository: mathcore.toml.
In the future, there may be more comprehensive documentation on a dedicated website.
Python package
Install the package with
pip install math-core
Basic documentation for the Python package can be found on pypi page.
Rust library
Add to your project with
cargo add math-core
The documentation for the library can be found on docs.rs: https://docs.rs/math-core/latest/math_core/
WebAssembly module
The WebAssembly frontend is currently only used for the playground. In the future, a package for this may be published to npm.
Required CSS
Specifying the math font
The MathML code generated by this project is intended to be very portable and work almost without a CSS style sheet. However, in order to really get LaTeX-like rendering of the MathML, one unfortunately needs custom math fonts.
To specify the font, include something like this in your CSS:
@font-face {
font-family: Libertinus Math Regular;
src: url('./LibertinusMath-Regular.woff2') format('woff2');
}
math {
font-family: "Libertinus Math Regular", math;
}
Some day, perhaps, any font with a MATH table will be supported, but right now fonts require some tweaks.
The main problem is that Chromium does not look at ssty variants when deciding on a glyph for super- and subscript (resulting in incorrectly rendered primes) and the fact that Chromium does not horizontally center accents. These problems have been manually fixed for the three fonts included in this project:
- New Computer Modern Math Book (original repo): a maintained continuation of LaTeX’s classic Computer Modern Math
- Libertinus Math (original repo): a maintained continuation of Linux Libertine
- Noto Sans Math (original repo): a sans-serif math font
The fixes applied to the font files do not change the shape of any glyphs; they merely rearrange some glyphs or center them. The font files can be found in the playground/ directory in this repository. To use them in your website, download them here and load them on the page from your server. No guarantees will be made that the fonts on the playground will remain available on the current URLs.
Font subsetting
The math fonts all have quite large font files. Especially New Computer Modern Math Book is enormous with an almost 700kB .woff2 file. Therefore, if possible, you should use font subsetting where the font file only includes those glyphs that are actually used on your website. Existing tools should work fine for this.
CSS for polyfills
Chromium does not support the <menclose> element, which is used for \sout{...}, \cancel{...}, etc. Therefore, if you want to use these commands, you need to include the following CSS:
/* Styles for Chromium only */
@supports (not (-webkit-backdrop-filter: blur(1px))) and (not (-moz-appearance: none)) {
menclose {
position: relative;
padding: 0.5ex 0;
}
mrow.menclose-updiagonalstrike,
mrow.menclose-downdiagonalstrike,
mrow.menclose-horizontalstrike {
display: inline-block;
position: absolute;
left: 0.5px;
bottom: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: currentcolor;
}
mrow.menclose-updiagonalstrike {
clip-path: polygon(0.05em 100%, 0 calc(100% - 0.05em), calc(100% - 0.05em) 0, 100% 0.05em);
}
mrow.menclose-downdiagonalstrike {
clip-path: polygon(0em 0.05em, 0.05em 0em, 100% calc(100% - 0.05em), calc(100% - 0.05em) 100%);
}
mrow.menclose-horizontalstrike {
clip-path: polygon(0em calc(55% + 0.0333em), 0em calc(55% - 0.0333em), 100% calc(55% - 0.0333em), 100% calc(55% + 0.0333em));
}
}
Dealing with other rendering problems
The above CSS unfortunately does not fix all rendering bugs found in the current versions of browsers. There is a tracking issue for other known rendering bugs: https://github.com/tmke8/math-core/issues/209
Development status
There are two tracking issues for development:
- Missing environments: https://github.com/tmke8/math-core/issues/154
- Missing commands: https://github.com/tmke8/math-core/issues/155
Other things that haven’t been implemented yet:
- Nested math mode (math mode within
\text{...}): https://github.com/tmke8/math-core/issues/431
Features that are not planned
There are some things we will (most likely) never support.
Infix commands like \over and \above
Supporting these would make the parser much more complicated. This does not seem worth it, given that these commands are very rarely used and considered somewhat deprecated.
Other commands in this category: \choose, \brace, \brack, \atop
Definition commands like \def, \newcommand, \definecolor
Again, supporting these would make the code much more complicated and anyway, these commands need to be repeated in every document. It seems more convenient to users and to the development of this project if new commands can only be defined in the config file.
Italic numbers, \mathit{012}
There is no Unicode range for this, so the only way to implement this would be with a custom font and a CSS class, which we would prefer to avoid.
Tips for writing LaTeX intended to be converted with this library
- Don’t use infix commands like
\over,\above,\choose,\brace,\brack,\atop. - Don’t try to create your own symbols by overlapping or stacking existing symbols; instead, try to find a Unicode symbol that looks like what you want: https://ftp.tu-chemnitz.de/pub/tex/fonts/newcomputermodern/doc/newcm-unimath-symbols.pdf
- This also applies to things like
:=. Consider using\coloneqqinstead, which will result in the semantically correct Unicode symbol.
- This also applies to things like
- Don’t worry about having unnecessary curly braces, like, say,
x_{2}vsx_2. Both result in the same MathML because unnecessary groups are stripped away by this library. - Try to avoid using absolute length units like
\hspace{1cm}. It’s difficult to render them correctly. Instead, use relative length units like\hspace{2.8em}.
Alternatives to this library
Note: at the time of this writing (June 2025), none of the following libraries render \vec and \hat correctly.
- pulldown-latex: The project most similar to this one. It is a Rust library for converting LaTeX math to MathML Core. The differences are:
- pulldown-latex only provides a Rust library; no Python package, no CLI
- pulldown-latex requires a CSS style sheet
- pulldown-latex can’t do certain simplifications of the MathML AST due to its architecture; for example, it can’t strip away the unnecessary grouping in
x_{2}, resulting in an unnecessary<mrow>in the output - At the time of this writing (June 2025), pulldown-latex doesn’t distinguish between
\mathcaland\mathscr.
- Temml: a fork of KaTeX which removed the HTML output of KaTeX and kept only on the MathML output. Temml produces much higher quality MathML output than KaTeX. The differences to this library are:
- Temml is written in JavaScript, with all the pros and cons that result from that
- Temml requires a CSS style sheet
- Temml is much more willing to work around browser bugs to get consistent rendering, with specific CSS hacks for each browser; math-core doesn’t do that yet and it’s not clear we’ll ever do that
Acknowledgments
This code was originally forked from https://github.com/osanshouo/latex2mathml. The basic architecture of a lexer and a parser remains, but all the details have drastically changed and the supported portion of LaTeX commands has drastically increased.