obfuse
| Crates.io | obfuse |
| lib.rs | obfuse |
| version | 1.0.1 |
| created_at | 2025-12-15 10:11:48.567471+00 |
| updated_at | 2026-01-17 12:27:29.345953+00 |
| description | Compile-time string obfuscation with runtime decryption and secure memory wiping |
| homepage | |
| repository | https://github.com/scc-tw/obfuse-rs |
| max_upload_size | |
| id | 1985804 |
| size | 65,902 |
documentation
README
obfuse-rs
Compile-time string encryption for Rust with runtime decryption and secure memory wiping.
🔒 Now with polymorphic decryption by default - Each string gets unique inline decryption code combining AES-256-GCM with random transformations for maximum anti-reversing protection.
Demo
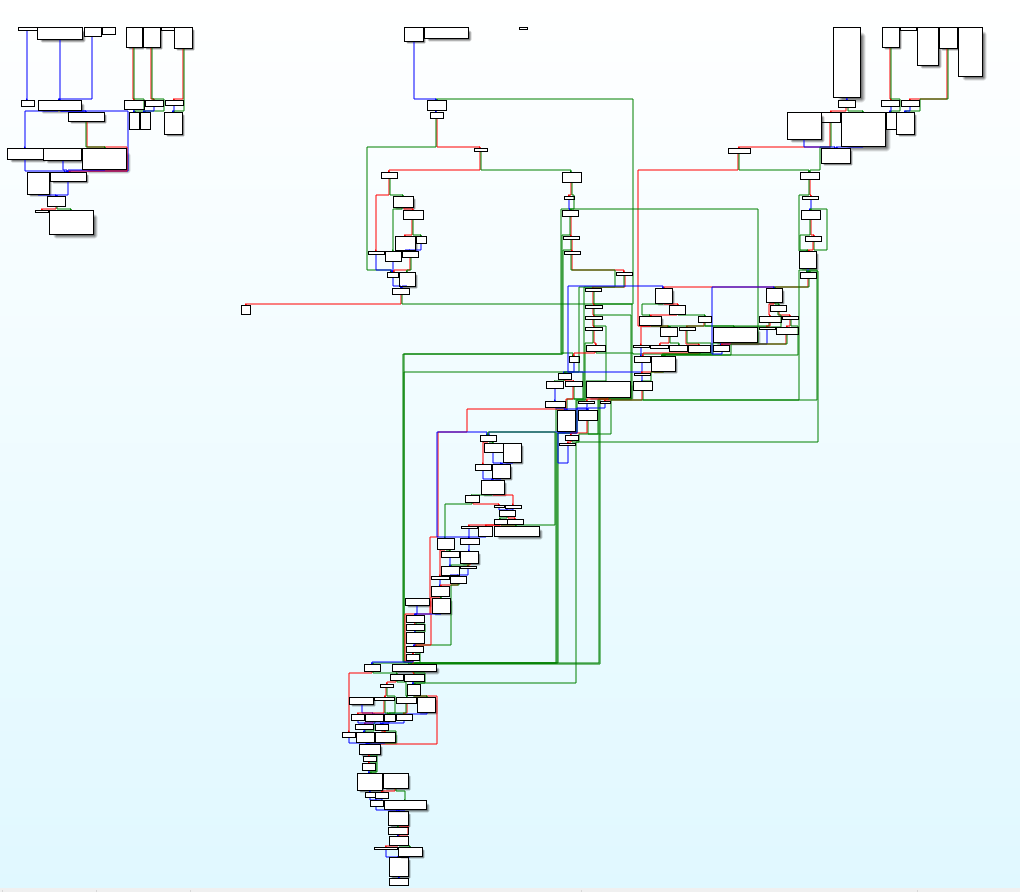
Control Flow Obfuscation in IDA Pro
Obfuscated binaries produce complex control flow graphs that resist static analysis:
Macro Expansion
The obfuse! macro generates unique inline decryption code for each string at compile time:
Quick Start
[dependencies]
obfuse = "1.0"
use obfuse::obfuse;
fn main() {
// String encrypted at compile time with AES-256-GCM + unique polymorphic layers
let license = obfuse!("Licensed to ACME Corp - Internal Use Only");
// Decrypted only when accessed
println!("{}", license.as_str());
// Memory securely wiped on drop
}
Security Notice: This library provides string obfuscation, not military-grade encryption. The encryption key is embedded in the binary alongside the ciphertext. A determined attacker with access to your binary can extract both.
Appropriate uses:
- Hiding license/copyright strings from casual inspection
- Obfuscating internal configuration or feature flags
- Making reverse engineering more time-consuming
- Protecting proprietary algorithms or logic identifiers
NOT appropriate for:
- Storing API keys, passwords, or credentials (use proper secrets management)
- Compliance requirements (PCI-DSS, HIPAA, SOC2, etc.)
- Any data where extraction would be catastrophic
Features
- Compile-time encryption: Strings are encrypted during compilation, never stored in plaintext in binaries
- Polymorphic decryption (default): Each string gets unique inline decryption code with combined encryption
- Control flow flattening (default): Decryption logic is transformed into state machines with opaque predicates and fake blocks, making static analysis extremely difficult
- Combined encryption layers (polymorphic mode):
- Layer 1: Strong AEAD encryption (AES-256-GCM by default)
- Layer 2: Unique polymorphic transformations per string (XOR, ADD/SUB, bit rotations)
- Layer 3: Runtime key derivation (keys computed from constants, not stored statically)
- Multiple encryption algorithms: Choose via Cargo features
aes-256-gcm(default) - AES-256 in GCM mode with polymorphic layersaes-128-gcm- AES-128 in GCM mode with polymorphic layerschacha20-poly1305- ChaCha20-Poly1305 AEAD with polymorphic layersxor- Simple XOR with MBA obfuscation (fast, less secure)
- MBA (Mixed Boolean-Arithmetic) transformations: XOR decryption uses mathematically equivalent but complex expressions to resist decompiler simplification (e.g., IDA's Hex-Rays)
- Proper error handling: No panics unless you use
.as_str()- usetry_as_str()for Result-based error handling - Secure memory handling: Volatile zeroing of data on drop
- Zero-copy decryption: Decrypt only when accessed
- No runtime dependencies: Encryption happens at compile time
Encryption Modes
Default Mode: AES-256-GCM + Polymorphic + Control Flow Flattening
The default configuration provides maximum obfuscation through combined techniques:
[dependencies]
obfuse = "1.0" # Uses aes-256-gcm + polymorphic + control-flow-flatten by default
Returns: ObfuseStrInline - each string has unique inline decryption code
Obfuscation layers:
- AES-256-GCM encryption: Industry-standard authenticated encryption
- Polymorphic transformations: 2-4 random layers per string (XOR, ADD/SUB, rotations)
- Control flow flattening: Decryption converted to state machines with opaque predicates
- Runtime key derivation: Keys computed from constants, not stored statically
- No central decrypt function: Each string has unique inline decryption code
Benefits:
- ✅ Maximum anti-reversing protection
- ✅ Defense in depth (multiple independent obfuscation layers)
- ✅ Unique code per string prevents pattern analysis
- ✅ Control flow graphs become extremely complex (see IDA screenshot above)
- ✅ Proper error propagation (no unwrap/expect in generated code)
Trade-offs:
- Slightly larger binary (~150 bytes per string vs ~68 bytes traditional)
- Minimal runtime overhead (key computation is fast)
Traditional Mode: AES-256-GCM Only
For projects that prioritize smaller binary size:
[dependencies]
obfuse = { version = "1.0", default-features = false, features = ["aes-256-gcm"] }
Returns: ObfuseStr - traditional centralized decryption
When to use:
- Binary size is critical
- Basic obfuscation is sufficient
- Not targeting experienced reverse engineers
Other Encryption Options
# AES-128-GCM with polymorphic (smaller key, still very secure)
obfuse = { version = "1.0", default-features = false, features = ["aes-128-gcm", "polymorphic"] }
# ChaCha20-Poly1305 with polymorphic (best for ARM/mobile)
obfuse = { version = "1.0", default-features = false, features = ["chacha20-poly1305", "polymorphic"] }
# XOR with MBA (fastest, suitable for obfuscation only)
obfuse = { version = "1.0", default-features = false, features = ["xor"] }
Recommendations by Use Case
| Use Case | Recommended Configuration | Return Type | Why |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production software | Default (aes-256-gcm + polymorphic) |
ObfuseStrInline |
Maximum protection, worth the small size increase |
| Mobile/embedded | chacha20-poly1305 + polymorphic |
ObfuseStrInline |
ChaCha20 is faster on ARM processors |
| Size-critical | aes-256-gcm only (no polymorphic) |
ObfuseStr |
Smallest per-string overhead |
| High-performance | xor with MBA |
ObfuseStr |
Fastest encryption/decryption |
| Maximum security | Default + deterministic seed for CI | ObfuseStrInline |
Reproducible builds with strong protection |
Binary Size Impact
Adding obfuse to your project has minimal overhead:
| Configuration | Library Overhead | Per-String Overhead | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Default (AES-256 + polymorphic) | ~27 KB | ~150 bytes | Recommended - Maximum security |
| Traditional (AES-256 only) | ~27 KB | ~68 bytes | Smaller, but less secure |
| XOR with MBA | ~5 KB | ~40 bytes | Fastest, obfuscation only |
Breakdown (default mode):
- Library overhead: ~27 KB (one-time cost for crypto + zeroize)
- Per-string overhead: ~150 bytes (inline decryption code + encrypted data)
For 100 strings:
- Traditional: 27 KB + (100 × 68 bytes) = ~34 KB
- Polymorphic (default): 27 KB + (100 × 150 bytes) = ~42 KB
- Extra cost: 8 KB for significantly stronger protection
Performance
| Operation | Time |
|---|---|
| First access (decryption) | ~500 ns |
| Cached access | ~10 ns |
| Plain string access | ~1 ns |
Decryption is lazy and cached - subsequent accesses are nearly free.
Installation
Requires Rust 1.85+ (edition 2024)
Add to your Cargo.toml:
[dependencies]
obfuse = "1.0" # Default: aes-256-gcm + polymorphic + control-flow-flatten
This gives you maximum obfuscation with:
- AES-256-GCM authenticated encryption
- Unique polymorphic transformations per string
- Control flow flattening (state machines + opaque predicates)
- Runtime key derivation
- No central decryption point
Customizing Encryption Options
If you need different configurations:
# Traditional mode (smaller binary, less secure)
[dependencies]
obfuse = { version = "1.0", default-features = false, features = ["aes-256-gcm"] }
# AES-128 with polymorphic (good balance)
[dependencies]
obfuse = { version = "1.0", default-features = false, features = ["aes-128-gcm", "polymorphic"] }
# ChaCha20 with polymorphic (best for ARM/mobile)
[dependencies]
obfuse = { version = "1.0", default-features = false, features = ["chacha20-poly1305", "polymorphic"] }
# XOR only (fastest, obfuscation only)
[dependencies]
obfuse = { version = "1.0", default-features = false, features = ["xor"] }
Understanding Polymorphic Mode (Enabled by Default)
Polymorphic mode generates unique inline decryption code for each string, eliminating central decryption functions that aid reverse engineering.
What it does:
- Layer 1: Encrypts with AES-256-GCM (industry-standard AEAD)
- Layer 2: Adds 2-4 random transformation layers per string
- Layer 3: Derives keys at runtime from constants
Why it's effective:
- Each string has unique decryption code (not a shared function)
- Reverse engineers must analyze each string individually
- Defense in depth: Multiple independent obfuscation layers
- No panics in generated code: Errors propagate properly via
Result
To disable polymorphic and use traditional mode only:
[dependencies]
obfuse = { version = "1.0", default-features = false, features = ["aes-256-gcm"] }
Understanding Control Flow Flattening (Enabled by Default)
Control flow flattening transforms the decryption logic into state machines that are extremely difficult to analyze statically.
What it does:
- Converts sequential decryption steps into a dispatcher loop
- Inserts opaque predicates (conditions that always evaluate one way but are hard to prove statically)
- Adds fake blocks that are never executed but appear valid
- Uses randomized state transitions
Why it's effective:
- IDA Pro and other disassemblers show complex control flow graphs (see demo above)
- Decompilers produce convoluted pseudo-code instead of clean logic
- Symbolic execution tools struggle with opaque predicates
- Each string has different state machine structure
To disable control flow flattening:
[dependencies]
obfuse = { version = "1.0", default-features = false, features = ["aes-256-gcm", "polymorphic"] }
Debug mode (cff-debug feature): Prints state machine structure during compilation for debugging.
Usage
Basic Usage (Polymorphic Mode - Default)
use obfuse::obfuse;
fn main() {
// Returns ObfuseStrInline with unique inline decryption code
let build_info = obfuse!("Build: 2024.1.0-internal");
// Decrypted only when accessed (may panic on error)
println!("{}", build_info.as_str());
// Memory is securely wiped when `build_info` goes out of scope
}
Error Handling (Recommended)
use obfuse::{obfuse, ObfuseError};
fn main() -> Result<(), ObfuseError> {
let license = obfuse!("Pro Edition - Licensed to Example Inc");
// Use try_as_str() for proper error handling - no panics!
match license.try_as_str() {
Ok(s) => println!("{s}"),
Err(ObfuseError::InvalidUtf8(e)) => {
eprintln!("Invalid UTF-8: {e}");
}
Err(e) => {
eprintln!("Decryption error: {e}");
}
}
Ok(())
}
Or with ? operator:
use obfuse::{obfuse, ObfuseError};
fn get_license() -> Result<String, ObfuseError> {
let license = obfuse!("Pro Edition");
Ok(license.try_as_str()?.to_string())
}
Traditional Mode Usage
use obfuse::{obfuse, ObfuseStr};
fn main() {
// Returns ObfuseStr when polymorphic is disabled
let endpoint: ObfuseStr = obfuse!("https://internal.example.com/api/v2");
// Use the decrypted string
connect_to_service(endpoint.as_str());
// `endpoint` is automatically zeroed on drop
}
With Explicit Type Annotation
use obfuse::obfuse;
fn main() {
// Type inference works for both modes
let version = obfuse!("v2.1.0-beta");
// Explicit type if needed (default mode returns ObfuseStrInline)
let copyright: _ = obfuse!("Copyright 2024 Example Corp");
println!("{}", version.as_str());
println!("{}", copyright.as_str());
}
Lazy Decryption
Both ObfuseStrInline and ObfuseStr decrypt lazily:
use obfuse::obfuse;
fn main() {
let config = obfuse!("feature_flags=premium,analytics");
// String remains encrypted until first access
if should_load_config() {
// Decryption happens here
parse_config(config.as_str());
}
// If condition is false, string is never decrypted
}
How It Works
-
Compile Time: The
obfuse!macro:- Generates a random encryption key and nonce
- Encrypts the string literal using the selected algorithm
- Embeds encrypted bytes, key, and nonce in the binary
-
Runtime: The
ObfuseStrtype:- Stores encrypted data until accessed
- Decrypts on first call to
as_str()orDeref - Caches decrypted value for subsequent accesses
-
Drop: When
ObfuseStris dropped:- Uses
std::ptr::write_volatileto zero all sensitive memory - Zeros: encryption key, nonce, and decrypted plaintext
- Prevents compiler from optimizing away the zeroing
- Uses
MBA (Mixed Boolean-Arithmetic) Transformations
When using the xor feature, decryption logic is obfuscated using MBA transformations to resist decompiler simplification.
What are MBA Transformations?
MBA transformations replace simple operations with mathematically equivalent but complex expressions. For example:
Simple XOR: a ^ b
MBA equivalent: (a | b) - (a & b)
With noise: ((a | b) + D1 - D1) - ((a & b) + D2 - D2) + (D3 ^ D3)
Why Use MBA?
Decompilers like IDA's Hex-Rays are excellent at recognizing and simplifying straightforward operations. MBA transformations:
- Resist pattern matching: The complex expressions don't match known simplification patterns
- Expand simple operations: A single XOR becomes many lines of arithmetic/logic
- Include noise operations: Dummy constants that cancel out add visual complexity
- Combine Boolean and arithmetic: Mixing
AND,OR,XORwith+,-,*prevents easy reduction
Example Decompiler Output
Without MBA, a simple decryption loop might decompile as:
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
plaintext[i] = ciphertext[i] ^ key[i % 32];
With MBA transformations, the same logic becomes dozens of lines of convoluted operations, making reverse engineering significantly more time-consuming.
Build Modes: Random vs Deterministic
This library supports two build modes for different use cases:
Default: Random Key (Recommended for Production)
// Random key generated each compile - different binary every build
let license = obfuse!("Licensed to ACME Corp");
println!("{}", license.as_str()); // Auto-decrypts
Build 1: key = [0xab, 0xcd, ...] (random)
Build 2: key = [0x12, 0x34, ...] (different random)
Build 3: key = [0x9f, 0xe2, ...] (different random)
Benefits:
- Each build produces unique encryption
- Harder for attackers to create universal decryption tools
- Best obfuscation for production binaries
With Seed: Deterministic Key (For Testing/CI)
// Same seed = same key = reproducible output
let license = obfuse!("Licensed to ACME Corp", seed = "test_seed_123");
println!("{}", license.as_str()); // Auto-decrypts (same as random mode)
Build 1 (seed="test"): key = [0xaa, 0xbb, ...] (deterministic)
Build 2 (seed="test"): key = [0xaa, 0xbb, ...] (same!)
Build 3 (seed="prod"): key = [0xcc, 0xdd, ...] (different seed = different key)
Benefits:
- Reproducible builds for CI/CD pipelines
- Testable encrypted output
- Debugging with known encryption state
Which Mode Should You Use?
| Use Case | Recommended |
|---|---|
| Production builds | obfuse!("...") (random) |
| Unit tests | obfuse!("...", seed = "test") |
| CI/CD pipelines | obfuse!("...", seed = "ci") |
| Debugging encryption issues | obfuse!("...", seed = "debug") |
Important: Both Modes Are Obfuscation
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Your Binary (Both Modes) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Encrypted Data: [0x4a, 0x7f, 0x2c, ...] │
│ Encryption Key: [0xab, 0xcd, 0xef, ...] ← HERE │
│ Nonce: [0x11, 0x22, 0x33, ...] │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Key is ALWAYS embedded in binary
This is OBFUSCATION, not real encryption
For actual secrets (API keys, passwords, credentials), use runtime secrets management (environment variables, Vault, AWS Secrets Manager).
Security Considerations
What This Protects Against
- Static binary analysis (strings command, hex editors)
- Simple memory dumps of unaccessed strings
- Casual reverse engineering attempts
What This Does NOT Protect Against
- Runtime memory inspection while string is in use
- Sophisticated reverse engineering
- Side-channel attacks
- Compromised systems with debugging access
Best Practices
- Use error handling: Prefer
try_as_str()overas_str()to avoid panics - Minimize lifetime: Keep obfuscated strings in scope only while needed
- Avoid cloning: Don't clone decrypted strings unnecessarily
- Use strong algorithms: Default (
aes-256-gcm+polymorphic) is recommended - Defense in depth: Use as one layer of protection, not the only one
API Reference
obfuse! Macro
// Random key (production) - Default returns ObfuseStrInline
obfuse!("string literal") -> ObfuseStrInline // with polymorphic (default)
obfuse!("string literal") -> ObfuseStr // without polymorphic
// Deterministic key (testing/CI) - Same return types
obfuse!("string literal", seed = "your_seed") -> ObfuseStrInline // or ObfuseStr
Encrypts a string literal at compile time.
- Without seed: Random key each compile (non-reproducible)
- With seed: Deterministic key derived from seed (reproducible)
- Return type:
ObfuseStrInline(default with polymorphic) orObfuseStr(traditional mode)
ObfuseStrInline Type (Polymorphic Mode - Default)
impl ObfuseStrInline {
/// Returns the decrypted string, decrypting on first access.
/// Panics on error - use try_as_str() for error handling.
pub fn as_str(&self) -> &str;
/// Fallible version - returns Result instead of panicking.
/// RECOMMENDED for all production code.
pub fn try_as_str(&self) -> Result<&str, ObfuseError>;
/// Returns the decrypted string as bytes.
/// Panics on error - use try_as_bytes() for error handling.
pub fn as_bytes(&self) -> &[u8];
/// Fallible version of as_bytes().
/// RECOMMENDED for all production code.
pub fn try_as_bytes(&self) -> Result<&[u8], ObfuseError>;
/// Returns true if the string has been decrypted.
pub fn is_decrypted(&self) -> bool;
/// Pre-decrypt without returning the value.
pub fn try_decrypt(&self) -> Result<(), ObfuseError>;
/// Manually zeros the decrypted plaintext memory.
pub fn zeroize(&mut self);
}
impl Deref for ObfuseStrInline {
type Target = str;
fn deref(&self) -> &str; // Triggers decryption, panics on error
}
impl Drop for ObfuseStrInline {
fn drop(&mut self); // Zeros decrypted plaintext
}
ObfuseStr Type (Traditional Mode)
impl ObfuseStr {
/// Returns the decrypted string, decrypting on first access.
/// Panics with detailed message on error.
pub fn as_str(&self) -> &str;
/// Fallible version - returns Result instead of panicking.
/// Recommended for critical code paths.
pub fn try_as_str(&self) -> Result<&str, ObfuseError>;
/// Returns the decrypted string as bytes.
pub fn as_bytes(&self) -> &[u8];
/// Fallible version of as_bytes().
pub fn try_as_bytes(&self) -> Result<&[u8], ObfuseError>;
/// Returns true if the string has been decrypted.
pub fn is_decrypted(&self) -> bool;
/// Pre-decrypt without returning the value.
pub fn try_decrypt(&self) -> Result<(), ObfuseError>;
/// Manually zero memory (also happens automatically on drop).
pub fn zeroize(&mut self);
}
impl Deref for ObfuseStr {
type Target = str;
fn deref(&self) -> &str; // Triggers decryption, panics on error
}
impl Drop for ObfuseStr {
fn drop(&mut self); // Volatile zeroing of all sensitive data
}
ObfuseError Type
/// Errors that can occur during decryption
#[derive(Debug)]
pub enum ObfuseError {
/// Memory allocation failed during decryption (OOM)
AllocationFailed,
/// AEAD authentication tag verification failed.
/// Indicates ciphertext tampering or algorithm mismatch.
AuthenticationFailed,
/// Decrypted bytes are not valid UTF-8
InvalidUtf8(std::str::Utf8Error),
}
impl std::fmt::Display for ObfuseError { /* ... */ }
impl std::error::Error for ObfuseError { /* ... */ }
Project Structure
obfuse-rs/
├── Cargo.toml # Workspace configuration
├── README.md
├── LICENSE
├── docs/
│ └── images/ # Documentation images (IDA screenshots, etc.)
├── scripts/ # Verification scripts
│ ├── verify_cff_obfuscation.sh
│ ├── verify_mba_obfuscation.sh
│ └── verify_polymorphic.sh
├── .github/
│ └── workflows/
│ ├── ci.yml # CI pipeline
│ └── publish.yml # Crates.io publishing
├── obfuse/ # Main library crate (re-exports)
│ ├── Cargo.toml
│ ├── src/
│ │ └── lib.rs
│ ├── examples/
│ │ ├── basic.rs
│ │ ├── deterministic.rs
│ │ ├── error_handling.rs
│ │ ├── hello.rs
│ │ └── polymorphic.rs
│ └── tests/
│ ├── binary_verification.rs
│ ├── cff_integration.rs
│ ├── integration.rs
│ └── polymorphic.rs
├── obfuse-macros/ # Procedural macro crate
│ ├── Cargo.toml
│ └── src/
│ ├── lib.rs
│ ├── encrypt.rs # Encryption code generation
│ ├── polymorphic.rs # Polymorphic transformation generation
│ └── control_flow_flatten/
│ ├── mod.rs
│ ├── block_scheduler.rs
│ ├── state_machine.rs
│ └── opaque_predicates.rs
└── obfuse-core/ # Core encryption/decryption logic
├── Cargo.toml
└── src/
├── lib.rs
├── error.rs # Error types (ObfuseError)
├── obfuse_str.rs # ObfuseStr type (traditional mode)
├── obfuse_str_inline.rs # ObfuseStrInline type (polymorphic mode)
├── mba.rs # MBA transformations
├── aes.rs # AES-128/256-GCM encryption
├── chacha.rs # ChaCha20-Poly1305 encryption
└── xor.rs # XOR encryption with MBA
Building
# Build with default features (AES-256-GCM)
cargo build
# Build with specific algorithm
cargo build --no-default-features --features chacha20-poly1305
# Run tests
cargo test
# Run tests for specific algorithm
cargo test --no-default-features --features aes-128-gcm
License
MIT License - see LICENSE for details.
Contributing
Contributions welcome! Please read the contributing guidelines first.
Acknowledgments
- aes-gcm - AES-GCM implementation
- chacha20poly1305 - ChaCha20-Poly1305 implementation
- zeroize - Secure memory zeroing patterns