opencc-fmmseg
| Crates.io | opencc-fmmseg |
| lib.rs | opencc-fmmseg |
| version | 0.8.4 |
| created_at | 2025-07-10 07:45:27.833722+00 |
| updated_at | 2026-01-04 02:36:34.073259+00 |
| description | High-performance OpenCC-based Chinese conversion using FMM (Forward Maximum Matching) segmentation. |
| homepage | https://github.com/laisuk/opencc-fmmseg |
| repository | https://github.com/laisuk/opencc-fmmseg |
| max_upload_size | |
| id | 1746008 |
| size | 3,293,467 |
documentation
README
opencc-fmmseg
opencc-fmmseg is a high-performance Rust-based engine for Chinese text conversion.
It combines OpenCC's lexicons with an
optimized Forward Maximum Matching (FMM) algorithm, suitable for:
- Traditional ↔ Simplified Chinese text conversion
- Lexicon-based segmentation
- CLI tools and system integration via C/C++ or Python bindings
🦀 Example (Rust)
use opencc_fmmseg::OpenCC;
fn main() {
let input = "汉字转换测试";
let opencc = OpenCC::new();
let output = opencc.convert(input, "s2t", false);
println!("{}", output); // 漢字轉換測試
}
📦 Download
Grab the latest version for your platform from the Releases page:
| Platform | Download Link |
|---|---|
| 🪟 Windows | opencc-fmmseg-{latest}-windows-x64.zip |
| 🐧 Linux | opencc-fmmseg-{latest}-linux-x64.tar.gz |
| 🍎 macOS | opencc-fmmseg-{latest}-macos-arm64.tar.gz |
Each archive contains:
README.txt
version.txt
bin/ # Command-line tools
lib/ # Shared library (.dll / .so / .dylib)
include/ # C API header + C++ helper header
✨ Features
- 📦 Unified CLI & Library — Convert between Simplified and Traditional Chinese via a single, consistent interface.
- 🔍 Lexicon-driven segmentation — Uses OpenCC dictionaries with maximum-matching (FMM) and phrase-level masking for accurate linguistic conversion.
- ⚡ High performance — Optimized with Rayon parallelism, bit-mask gating (
key_length_mask,starter_len_mask), and zero-copy string views for near-native throughput. - 🧠 Smart gating engine — Automatically skips impossible probes using global and per-starter length masks, ensuring consistent O(n) scaling.
- 🧩 Modular integration — Usable as a Rust crate, C API (FFI), or Qt/.NET/Python binding with identical behavior across platforms.
- 🛠️ Lightweight & dependency-free — Pure Rust core, no external runtime or I/O overhead.
- 📄 Cross-platform ready — Builds cleanly on Windows, Linux, and macOS (x86_64 / ARM64), with CLI and shared-library distributions.
Installation
git clone https://github.com/laisuk/opencc-fmmseg
cd opencc-fmmseg
cargo build --release --workspace
🚀 CLI Usage
The CLI tool will be located at:
target/release/
opencc-rs # CLI plain text and Office document text converter
opencc-clip # Convert from clipboard, auto detect config
dict-generate # Generate dictionary ZSTD, CBOR or JSON files
Usage
opencc-rs convert
Convert plain text using OpenCC
Usage: opencc-rs.exe convert [OPTIONS] --config <config>
Options:
-i, --input <file> Input file (use stdin if omitted for non-office documents)
-o, --output <file> Output file (use stdout if omitted for non-office documents)
-c, --config <config> Conversion configuration [possible values: s2t, t2s, s2tw, tw2s, s2twp, tw2sp, s2hk, hk2s, t2tw, t2twp, t2hk, tw2t, tw2tp, hk2t, t2jp, jp2t]
-p, --punct Enable punctuation conversion
--in-enc <in_enc> Encoding for input [default: UTF-8]
--out-enc <out_enc> Encoding for output [default: UTF-8]
-h, --help Print help
opencc-rs office
Convert Office or EPUB documents using OpenCC
Usage: opencc-rs.exe office [OPTIONS] --config <config>
Options:
-i, --input <file> Input file (use stdin if omitted for non-office documents)
-o, --output <file> Output file (use stdout if omitted for non-office documents)
-c, --config <config> Conversion configuration [possible values: s2t, t2s, s2tw, tw2s, s2twp, tw2sp, s2hk, hk2s, t2tw, t2twp, t2hk, tw2t, tw2tp, hk2t, t2jp, jp2t]
-p, --punct Enable punctuation conversion
-f, --format <ext> Force document format: docx, odt, epub...
--keep-font Preserve original font styles
--auto-ext Infer format from file extension
-h, --help Print help
Example
Plain Text
./opencc-rs convert -c s2t -i text_simplified.txt -o text_traditional.txt
Office Documents or EPUB
- Supported OpenDocument formats:
.docx,.xlsx,.pptx,.odt,.ods,.odp,.epub
./opencc-rs office -c s2t --punct --format docx -i doc_simplified.docx -o doc_traditional.docx
- Supported conversions:
s2t– Simplified to Traditionals2tw– Simplified to Traditional Taiwans2twp– Simplified to Traditional Taiwan with idiomst2s– Traditional to Simplifiedtw2s– Traditional Taiwan to Simplifiedtw2sp– Traditional Taiwan to Simplified with idioms- etc
Lexicons
By default, it uses OpenCC's built-in lexicon paths. You can also provide your own lexicon dictionary generated by
dict-generate CLI tool.
📚 Library Usage
You can also use opencc-fmmseg as a library:
To use opencc-fmmseg in your project, add this to your Cargo.toml:
[dependencies]
opencc-fmmseg = "0.8.4" # or latest version
Then use it in your code:
use opencc_fmmseg::{OpenCC};
use opencc_fmmseg::OpenccConfig;
fn main() {
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Sample UTF-8 input (same spirit as C / C++ demos)
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
let input_text = "意大利邻国法兰西罗浮宫里收藏的“蒙娜丽莎的微笑”画像是旷世之作。";
println!("Text:");
println!("{}", input_text);
println!();
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Create OpenCC instance
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
let converter = OpenCC::new();
// Detect script
let input_code = converter.zho_check(input_text);
println!("Text Code: {}", input_code);
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Test 1: Legacy string-based config (convert)
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
let config_str = "s2twp";
let punct = true;
println!();
println!(
"== Test 1: convert(config = \"{}\", punctuation = {}) ==",
config_str, punct
);
let output1 = converter.convert(input_text, config_str, punct);
println!("Converted:");
println!("{}", output1);
println!("Converted Code: {}", converter.zho_check(&output1));
println!(
"Last Error: {}",
OpenCC::get_last_error().unwrap_or_else(|| "<none>".to_string())
);
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Test 2: Strongly typed config (convert_with_config)
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
let config_enum = OpenccConfig::S2twp;
println!();
println!(
"== Test 2: convert_with_config(config = {:?}, punctuation = {}) ==",
config_enum, punct
);
let output2 = converter.convert_with_config(input_text, config_enum, punct);
println!("Converted:");
println!("{}", output2);
println!("Converted Code: {}", converter.zho_check(&output2));
println!(
"Last Error: {}",
OpenCC::get_last_error().unwrap_or_else(|| "<none>".to_string())
);
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Test 3: Invalid config (string) — self-protected
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
let invalid_config = "what_is_this";
println!();
println!(
"== Test 3: invalid string config (\"{}\") ==",
invalid_config
);
let output3 = converter.convert(input_text, invalid_config, true);
println!("Returned:");
println!("{}", output3);
println!(
"Last Error: {}",
OpenCC::get_last_error().unwrap_or_else(|| "<none>".to_string())
);
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Test 4: Clear last error and verify state reset
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
println!();
println!("== Test 4: clear_last_error() ==");
OpenCC::clear_last_error();
println!(
"Last Error after clear: {}",
OpenCC::get_last_error().unwrap_or_else(|| "<none>".to_string())
);
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Summary
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
println!();
println!("All tests completed.");
}
Output:
Text:
意大利邻国法兰西罗浮宫里收藏的“蒙娜丽莎的微笑”画像是旷世之作。
Text Code: 2
== Test 1: convert(config = "s2twp", punctuation = true) ==
Converted:
義大利鄰國法蘭西羅浮宮裡收藏的「蒙娜麗莎的微笑」畫像是曠世之作。
Converted Code: 1
Last Error: <none>
== Test 2: convert_with_config(config = S2twp, punctuation = true) ==
Converted:
義大利鄰國法蘭西羅浮宮裡收藏的「蒙娜麗莎的微笑」畫像是曠世之作。
Converted Code: 1
Last Error: <none>
== Test 3: invalid string config ("what_is_this") ==
Returned:
Invalid config: what_is_this
Last Error: Invalid config: what_is_this
== Test 4: clear_last_error() ==
Last Error after clear: <none>
📦 Crate: opencc-fmmseg on crates.io
📄 Docs: docs.rs/opencc-fmmseg
🧩 C/C++ Integration (opencc_fmmseg_capi)
You can also use opencc-fmmseg via a C API for integration with C/C++ projects.
The zip includes:
- {lib}
opencc_fmmseg_capi.{so,dylib,dll} - C API:
opencc_fmmseg_capi.h - Header-only C++ helper:
OpenccFmmsegHelper.hpp
You can link against the shared library and call the segmentation/convert functions from any C or C++ project.
Example 1 (minimal C usage)
#include <stdio.h>
#include "opencc_fmmseg_capi.h"
int main(void) {
void *handle = opencc_new();
const char *config = "s2t";
const char *input = u8"汉字";
char *result = opencc_convert(handle, input, config, false);
printf("Input : %s\n", input);
printf("Converted: %s\n", result);
opencc_string_free(result);
opencc_delete(handle);
return 0;
}
Example 2 (detection + conversion)
##include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "opencc_fmmseg_capi.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
void *opencc = opencc_new();
bool is_parallel = opencc_get_parallel(opencc);
printf("OpenCC is_parallel: %d\n", is_parallel);
const char *config = u8"s2twp";
const char *text = u8"意大利邻国法兰西罗浮宫里收藏的“蒙娜丽莎的微笑”画像是旷世之作。";
printf("Text: %s\n", text);
int code = opencc_zho_check(opencc, text);
printf("Text Code: %d\n", code);
char *result = opencc_convert(opencc, text, config, true);
code = opencc_zho_check(opencc, result);
char *last_error = opencc_last_error();
printf("Converted: %s\n", result);
printf("Text Code: %d\n", code);
printf("Last Error: %s\n", last_error == NULL ? "No error" : last_error);
if (last_error != NULL) opencc_error_free(last_error);
if (result != NULL) opencc_string_free(result);
opencc_delete(opencc);
return 0;
}
Output
OpenCC is_parallel: 1
Text: 意大利邻国法兰西罗浮宫里收藏的“蒙娜丽莎的微笑”画像是旷世之作。
Text Code: 2
Converted: 義大利鄰國法蘭西羅浮宮裡收藏的「蒙娜麗莎的微笑」畫像是曠世之作。
Text Code: 1
Last Error: No error
Notes
-
opencc_new()creates and initializes a new OpenCC-FMMSEG instance. -
opencc_convert(...)is the legacy string-based API:- Uses a string config such as
"s2t","t2s","s2twp". - If the config is invalid, the conversion is blocked and an error string
(
"Invalid config: ...") is returned. - On success, any previous error state is automatically cleared.
- Uses a string config such as
-
opencc_convert_cfg(...)is the recommended API for new code:- Uses a numeric config (
opencc_config_t) instead of strings. - Avoids runtime string parsing and is more FFI-friendly.
- Invalid configs return a readable error string and set the last error.
- Uses a numeric config (
-
opencc_convert_cfg_mem(...)is an advanced buffer-based API:- Designed for bindings and performance-sensitive code.
- Uses a size-query + caller-allocated buffer pattern.
- Output length is data-dependent and cannot be predicted without running a first pass of the conversion logic.
- The required buffer size (including
'\0') is reported viaout_required. - The output buffer is owned and freed by the caller.
- For guaranteed success, callers should first perform a size-query
call with
out_buf = NULLandout_cap = 0. - For one-pass usage, callers may provide a buffer larger than the input (e.g. input length + ~10%), but must be prepared to retry if the buffer is insufficient.
- This API does not replace the
char*-returning APIs.
-
All input and output strings use null-terminated UTF-8 encoding.
-
punctuationaccepts standard C Boolean values (true/false) via<stdbool.h>. -
opencc_string_free(...)must be used to free strings returned by:opencc_convert(...)opencc_convert_cfg(...)opencc_last_error(...)
-
opencc_error_free(...)frees memory returned byopencc_last_error()only. It does not clear the internal error state. -
opencc_clear_last_error()clears the internal error state:- After calling this,
opencc_last_error()will return"No error". - This function does not free any previously returned error strings.
- It cannot replace
opencc_error_free().
- After calling this,
-
opencc_last_error()returns the most recent error message:- Returns a newly allocated string.
- Returns
"No error"if no error is recorded. - The returned string must always be freed with
opencc_error_free().
-
opencc_delete(...)destroys the OpenCC instance and frees its resources. -
opencc_zho_check(...)detects the script of the input text:1= Traditional Chinese2= Simplified Chinese0= Other / Undetermined
-
Parallel mode can be queried using
opencc_get_parallel()and modified usingopencc_set_parallel(...).
Project Structure
src/lib.rs– Main library with segmentation logic.capi/opencc-fmmseg-capiC API source and demo.tools/opencc-rs/src/main.rs– CLI tool (opencc-rs) implementation.dicts/– OpenCC text lexicons which converted into Zstd compressed CBOR format.
🛠 Built With
- Rust + Cargo Workspaces
- OpenCC-compatible dictionaries
- Parallelized FMM segmentation
- GitHub Actions cross-platform release automation
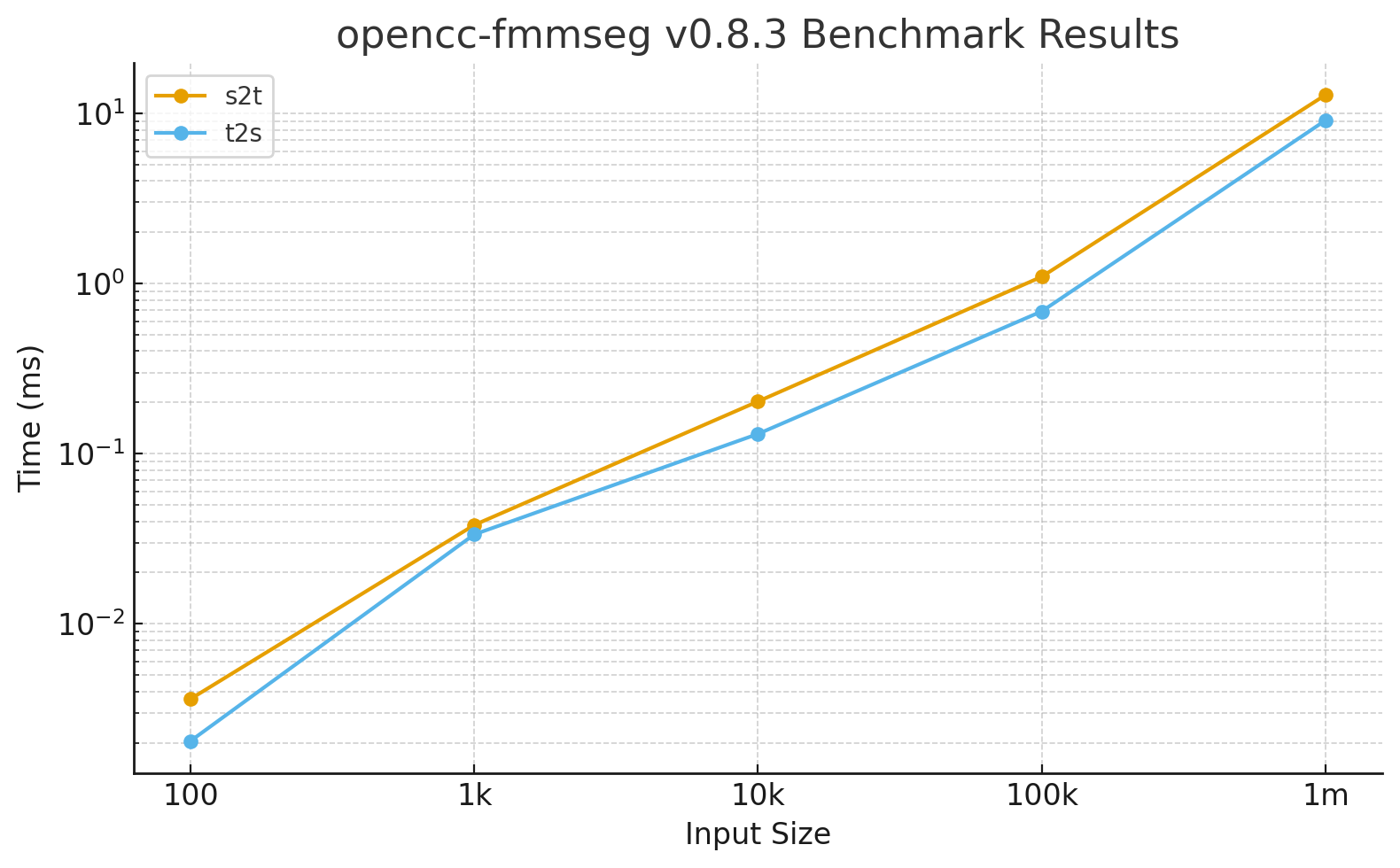
🚀 Benchmark Results: opencc-fmmseg Conversion Speed
Tested using Criterion.rs on 1.2 million characters with
punctuation disabled (punctuation = false), built in release mode with Rayon enabled.
Results from v0.8.3:
| Input Size | s2t Mean Time | t2s Mean Time |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 3.62 µs | 2.05 µs |
| 1,000 | 38.06 µs | 33.50 µs |
| 10,000 | 202.66 µs | 130.58 µs |
| 100,000 | 1.096 ms | 0.686 ms |
| 1,000,000 | 12.822 ms | 9.089 ms |
📊 Throughput Interpretation
- t2s: ≈ 110 million chars/sec
- s2t: ≈ 78 million chars/sec
- Equivalent to ~150–200 MB/s UTF-8 text throughput
- ≈ 200 full-length novels (500 k chars each) per second
- ≈ 1 GB of text converted in under 7 seconds
At this level, CPU saturation is negligible — I/O or interop overhead (file/clipboard/network) now dominates
runtime.
The new mask-first gating (key_length_mask + starter_len_mask) delivers perfect O(n) scaling and
ultra-stable parallel throughput across large text corpora.
🏅 Highlights
Credits
- OpenCC by BYVoid Carbo Kuo – Lexicon source.
📜 License
- MIT License.
- © Laisuk Lai.
- See LICENSE for details.
- See THIRD_PARTY_NOTICES.md for bundled OpenCC lexicons (Apache License 2.0).
💬 Feedback / Contributions
- Issues and pull requests are welcome.
- If you find this tool useful, please ⭐ star the repo or fork it.





