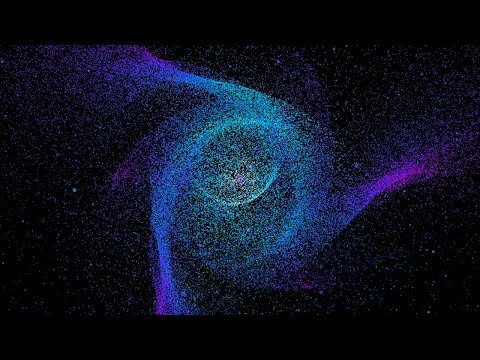
physim-core
| Crates.io | physim-core |
| lib.rs | physim-core |
| version | 0.4.1 |
| created_at | 2025-10-19 07:48:28.358589+00 |
| updated_at | 2025-10-19 08:03:37.849211+00 |
| description | Library for creating N-Body physics simulations |
| homepage | |
| repository | https://github.com/jhb123/physim |
| max_upload_size | |
| id | 1890170 |
| size | 97,878 |
documentation
README
██████╗ ██╗ ██╗██╗ ██╗███████╗██╗███╗ ███╗
██╔══██╗██║ ██║╚██╗ ██╔╝██╔════╝██║████╗ ████║
██████╔╝███████║ ╚████╔╝ ███████╗██║██╔████╔██║
██╔═══╝ ██╔══██║ ╚██╔╝ ╚════██║██║██║╚██╔╝██║
██║ ██║ ██║ ██║ ███████║██║██║ ╚═╝ ██║
╚═╝ ╚═╝ ╚═╝ ╚═╝ ╚══════╝╚═╝╚═╝ ╚═╝
An extensible framework for performing N-body simulations.
Overview
Physim provides a framework for users to run N-body simulations. Users can build pipelines from the command line or from a configuration file.
The functionality of physim can be expanded with plugins to add functionality. Developers can make these plugins with Rust and there is support for some elements to be written in languages with a C ABI. Physim comes with a variety of useful elements such as OpenGL renderers and gravity calculations.
There are two programs
physimruns simulations.physcanprovides documentation for elements.
The elements which come by default are:
astro: astro2 transform
astro: simple_astro transform
astro: solar initialiser
astro: star initialiser
astro: astro transform
astro: plummer initialiser
astro: cube initialiser
glrender: glrender renderer
glrender: stdout renderer
integrators: euler integrator
integrators: rk4 integrator
integrators: verlet integrator
mechanics: impulse transform
mechanics: shm transform
mechanics: collisions transmute
utilities: wrapper transmute
utilities: bpm transmute
utilities: idset transmute
utilities: csvsink renderer
utilities: bbox transmute
Installation
You are required to build physim from source. Install Rust, and the install script will install physim, physcan and the default plugins to $HOME/physim
chmod 755 install.sh
./install.sh
Running a simulation
physim simulations can be configured directly in the CLI. Each element is delimited by !, and the properties of the element can be configured as shown in the following example:
physim cube n=100000 seed=1 spin=1000 ! star mass=100000.0 radius=0.1 z=0.5 x=0.2 y=0.2 ! star mass=100000.0 radius=0.1 z=0.5 x=-0.2 y=-0.2 ! astro2 theta=1.5 e=0.5 ! verlet ! glrender ! global dt=0.00001 iterations=10000
Alternatively, the can be loaded via a file. The pipeline above can be expressed in toml as
[global]
dt = 0.00001
iterations = 1000
[elements]
[[elements.cube]]
n = 100000
seed = 1
spin = 1000
[[elements.astro2]]
theta = 1.5
e = 0.5
[[elements.star]]
mass = 100000.0
x=0.2
y=0.2
z=0.5
radius = 0.1
[[elements.star]]
mass = 100000.0
x=-0.2
y=-0.2
z=0.5
radius = 0.1
[[elements.verlet]]
[[elements.glrender]]
and run with
physim -f pipeline.toml
Encoding with FFMPEG
The following example shows how to use the stdout element from the glrender plugin.
physim cube n=100000 seed=1 spin=500 ! star mass=100000.0 x=0.1 y=0.1 radius=0.1 z=0.5 ! star mass=100000.0 x=-0.1 y=-0.1 radius=0.1 z=0.5 ! star mass=100000.0 x=-0.1 y=0.1 z=0.5 ! star mass=100000 x=0.1 y=-0.1 z=0.5 ! astro theta=1.3 ! verlet ! stdout zoom=1.5 resolution=1080p | ffmpeg -y -f rawvideo -pixel_format bgra -video_size 1920x1080 -framerate 60 -i pipe:0 -vf "scale=in_range=full:out_range=full,format=yuv420p10le" -c:v libx265 -preset slow -pix_fmt yuv420p10le output.mp4
Add audio with ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -i input.mp3 -c:v copy -c:a aac -shortest output.mp4
Element documentation
By default, plugins will be loaded from the directory that physim is in. However, you can specify additional directories, each one separated by :, with the PHYSIM_PLUGIN_DIR environment variable. To determine what elements you have access to, run
# Brief summary of all available elements
physcan
# More details about an element e.g. 'cube'
physcan cube
Development
debug plugin
The debug plugin is for ad-hoc manual testing. It can serve as poorly written documentation of how to use most features of physim. It is not built by default as it does not have anything very useful outside of a development context in it. To build it, you can run.
cargo build -p debug
cbindgen
Run cbindgen --lang c --crate physim-core --output physim.h to generate a header file.
Git
Commits should follow the conventional commits standard.
The .gitmessage file provides guidance on this and it can be set
as your template with
$ git config commit.template .gitmessage
We use the rebase strategy for pull requests.
Use pre-commit to keep the codebase free of common style issues.
Licence
MIT.
Roadmap
These features could result in Entity changing, so it is worth reiterating that this library is not in a stable form and backwards compatibility is not guaranteed.
- Bird flocking using the boids model.
- Calculation of gravitational potential using the fast multipole method.
- Gas simulation with the Lennard-Jones potential.
- Relativistic simulation using Einstein–Infeld–Hoffmann equations of motion.
- Element for rendering text as entities.
- General purpose test tools for pipeline and element testing.
- Improve use as a library.
- Electromagnetism.