polars_excel_writer
| Crates.io | polars_excel_writer |
| lib.rs | polars_excel_writer |
| version | 0.22.0 |
| created_at | 2023-08-20 14:40:33.459217+00 |
| updated_at | 2025-11-17 20:37:54.517209+00 |
| description | A Polars extension to serialize dataframes to Excel xlsx files |
| homepage | |
| repository | https://github.com/jmcnamara/polars_excel_writer |
| max_upload_size | |
| id | 949405 |
| size | 543,474 |
documentation
README
polars_excel_writer
The polars_excel_writer crate is a library for serializing Polars dataframes
to Excel Xlsx files.
The crate uses rust_xlsxwriter to do the Excel serialization and is
typically 5x faster than Polars when exporting large dataframes to Excel.
It provides a primary interface PolarsExcelWriter which is a configurable
Excel serializer that resembles the interface options provided by the Polars
write_excel() dataframe method.
Example
An example of writing a Polar Rust dataframe to an Excel file using the
PolarsExcelWriter interface.
use chrono::prelude::*;
use polars::prelude::*;
use polars_excel_writer::PolarsExcelWriter;
fn main() -> PolarsResult<()> {
// Create a sample dataframe for the example.
let df: DataFrame = df!(
"String" => &["North", "South", "East", "West"],
"Integer" => &[1, 2, 3, 4],
"Float" => &[4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0],
"Time" => &[
NaiveTime::from_hms_milli_opt(2, 59, 3, 456).unwrap(),
NaiveTime::from_hms_milli_opt(2, 59, 3, 456).unwrap(),
NaiveTime::from_hms_milli_opt(2, 59, 3, 456).unwrap(),
NaiveTime::from_hms_milli_opt(2, 59, 3, 456).unwrap(),
],
"Date" => &[
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 1).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 2).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 3).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 4).unwrap(),
],
"Datetime" => &[
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 1).unwrap().and_hms_opt(1, 0, 0).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 2).unwrap().and_hms_opt(2, 0, 0).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 3).unwrap().and_hms_opt(3, 0, 0).unwrap(),
NaiveDate::from_ymd_opt(2022, 1, 4).unwrap().and_hms_opt(4, 0, 0).unwrap(),
],
)?;
// Create a new Excel writer.
let mut excel_writer = PolarsExcelWriter::new();
// Write the dataframe to Excel.
excel_writer.write_dataframe(&df)?;
// Save the file to disk.
excel_writer.save("dataframe.xlsx")?;
Ok(())
}
Output file:
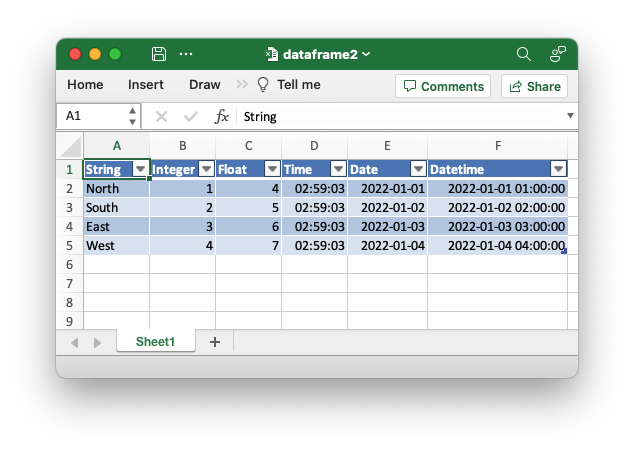
Performance
The table below shows the performance of writing a dataframe using Python
Polars, Python Pandas and PolarsExcelWriter.
| Test Case | Time (s) | Relative (%) |
|---|---|---|
Polars |
6.49 | 100% |
Pandas |
10.92 | 168% |
polars_excel_writer |
1.22 | 19% |
polars_excel_writer + zlib |
1.08 | 17% |
See the Performance section of the docs for more detail.