rufet
| Crates.io | rufet |
| lib.rs | rufet |
| version | 0.1.1 |
| created_at | 2022-01-15 11:50:14.205798+00 |
| updated_at | 2022-01-16 14:21:20.844488+00 |
| description | A command-line system information fetcher |
| homepage | https://github.com/GreenTeaSeb/rufet |
| repository | https://github.com/GreenTeaSeb/rufet |
| max_upload_size | |
| id | 514267 |
| size | 99,548 |
documentation
README
RUFET
Another command-line system information tool, but written in Rust!
Contents
Roadmap
Things planned for the future
Code
- Ansi image
- Real image support (Kitty,ueberzug)
- Sixel support
Inbuilt modules
- Hostname
- Kernel
- Memory
- OS
- Uptime
- Custom user scripts
- Common Environment variables
- editor
- terminal
- Terminal colors
- WM
- DE
- Packages
- Themes - gtk, Qt
- Resolution
- GPU
Documentation
- Documentation on docs.rs
- Better markdown
- Instructions for config
- Logo design
- Config examples, screenshots
Installation
cargo install rufet
or manually clone the repo and build
Configuration
Configuration is done via a toml file located at $HOME/.config/rufet/config.toml
Everything is separated into modules, such as [data], [logo],[data.hostname], and each of these modules has variables that dictate how the module will be displayed. Some of the modules have unique variables. Those variables will be mentioned below.
[data]
format="$hostname$os"
height=10
margin=2
padding=5
[data.hostname]
format="this is my hostname: $value"
[logo]
format="logo"
[[logo.rule]]
id="logo"
exec='echo -ne "$(<$HOME/.config/rufet/ansi)" \\n'
Variables
format
Changes the text that the module will display. Each module will replace $value with the value of what the module fetches. So hostname will replace $value with the hostname of the user.
[data.hostname]
format="This is my hostname: $value"
height
Changes the minimum number of lines the module takes up. Useful if you want to have some space between the module and it's border, or if you want to make the data modules be the same height as the logo. [data] height=25
padding
Adds blanks characters to the left and right of the module but within the border, useful if you want some space between the module and the border to the sides. [data.kernel] padding=25
margin
Adds blanks characters to the left and right of the module but outside the border, useful if you want some space between 2 modules separated by borders [data] margin=2
alignment
Changes the way the text inside a module is aligned [data] alignment= "left"|"center"|"right"
Unique variables
Data
the data module, which holds all the modules has inbuilt ids for each of the module $hostname,$os etc.
but it also has $all which will display all of the available modules that have not yet been used. So if you want to always display your memory usage first, you'd do format="$memory$all"
Uptime
Uptime has a variable time_format which formats the time it displays.
Example: time_format="Uptime is: $d days, $h hours, $m minutes, $s seconds"
Customizing the border
The border is a structure inside each module. It has it's own variables which can be customized like so:
[data.hostname.border]
top: ['╭', '─', '╮'],
bottom: ['╰', '─', '╯'],
sides: ['│', '│'],
visible: true,
color: "#ff00ff",
background: "255;0;0",
Rules
If you want to have a custom module that displays text, or executes a script, you do so via rules, a rule is a a structure which has an id , which, when found in other modules will be replaced with a value.
Rules can be used to make custom modules or to change the color and appearance of existing modules.
Variables for a rule:
id: "id to replace"
text: "text"
exec: "shell command"
color: "#fff"|"0;0;0"
background: "#fff"|"0;0;0"
effects: ["bold","faint","italic","underline","blink","reverse","conceal","crossed"]
border: Border
padding: int
margin: int
alignment: String
If the text variable isn't set, it will replace id with itself, while giving it the color. Useful if you want to change the color of a predefined id, like $value
the text variable has priority over exec,
Changing colors
Change the value of the color and background variables, they support hex code colors such as #f0f and #ff00ff , and rgb seperated by a ; , such as 255;0;255
[data.hostname]
format="this is my red hostname: $value , $blue"
[[data.hostname.rule]]
id="$value"
color="#ff0000"
[[data.hostname.rule]]
id="$blue"
text="this is blue text with a green background"
color="#0000ff"
background="#00ff00"
Custom modules
Custom modules are still rules, but instead of using the text variable to choose the id, you use the exec variable to execute a shell command that prints to the standard output.
[data]
format="$custom1"
[[data.rule]]
id="$custom1"
exec="echo -n aaa"
padding=5
[data.rule.border]
color="#f00"
visible=true
ANSI logo
Due to the way toml is made, it doesn't support the \e escape code used for ANSI art, or any other escape code used for it, the only way to get ANSI art inside a toml is with the \u001B escape code, for that you'd have to use an image to ANSI converter and then replace all of the escape codes with \u001B , instead of that, it's recommended to use a rule which then uses a command to print the contents of the file, such as echo, or any script of your choice. That will make it easier and also make the config file less clustered.
[logo]
format="logo"
[[logo.rule]]
id="logo"
exec='echo -ne "$(<$HOME/.config/rufet/ansi)" \\n'
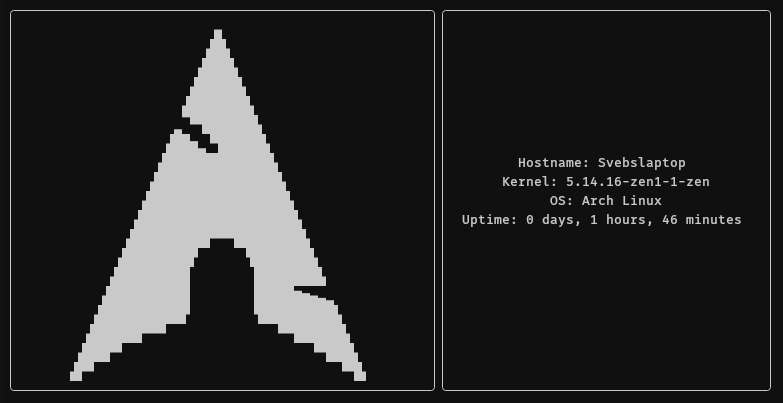
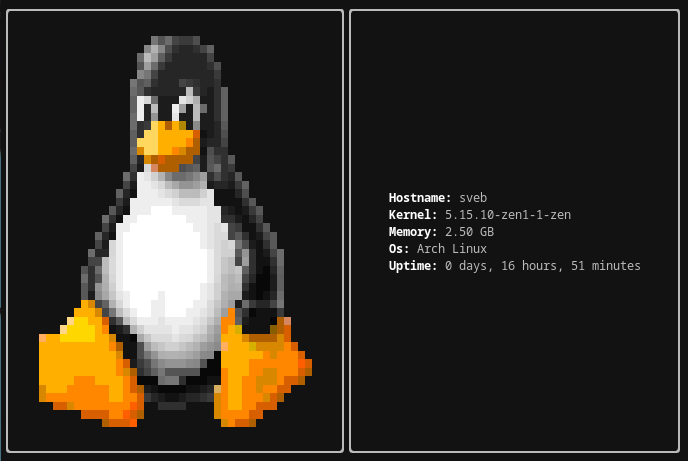
Screenshots