sahomedb
| Crates.io | sahomedb |
| lib.rs | sahomedb |
| version | 0.4.0 |
| created_at | 2024-07-23 11:32:18.558923+00 |
| updated_at | 2024-08-18 14:06:09.367103+00 |
| description | Fast embedded vector database with incremental HNSW indexing. |
| homepage | https://sahome.com/ |
| repository | https://github.com/Sahomey-Technologies/sahomedb |
| max_upload_size | |
| id | 1312682 |
| size | 229,247 |
documentation
README
👋 Meet SahomeDB
SahomeDB is a SQLite-inspired lightweight and easy to use embedded vector database. It is designed to be embedded directly inside your AI application. It is written in Rust and uses Sled as its persistence storage engine to save vector collections to the disk.
SahomeDB implements HNSW (Hierachical Navigable Small World) as its indexing algorithm. It is a state-of-the-art algorithm that is used by many vector databases. It is fast and scales well to large datasets.
Why SahomeDB?
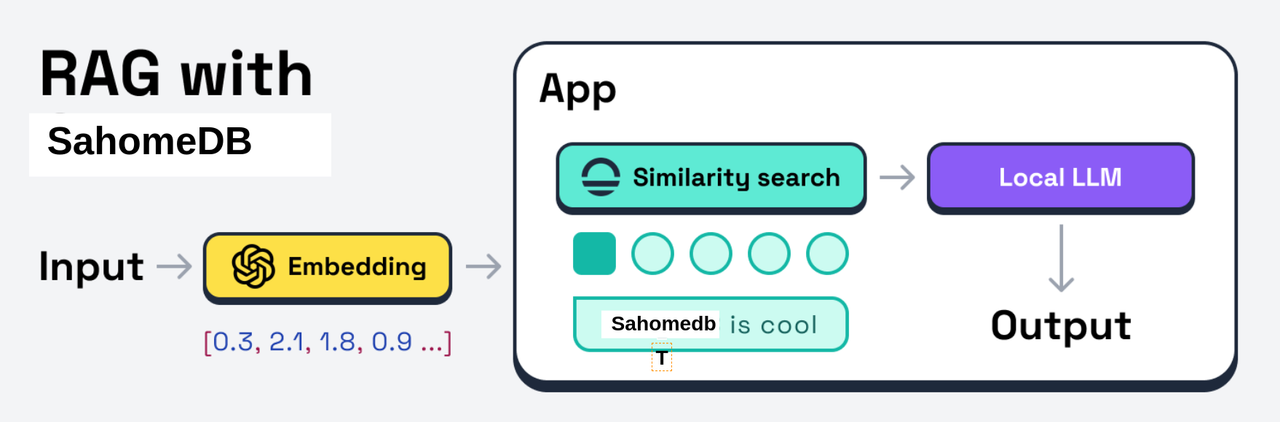
SahomeDB is very flexible for use cases related with vector search such as using RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) method with an LLM to generate a context-aware output. These are some of the reasons why you might want to use SahomeDB:
⭐️ Embedded database: SahomeDB doesn't require you to set up a separate server and manage it. You can embed it directly into your application and use its simple API like a regular library.
⭐️ Optional persistence: You can choose to persist the vector collection to the disk or keep it in memory. By default, whenever you use a collection, it will be loaded to the memory to ensure that the search performance is high.
⭐️ Incremental operations: SahomeDB allows you to add, remove, or modify vectors from collections without having to rebuild indexes. This allows for a more flexible and efficient approach on storing your vector data.
⭐ Flexible schema: Along with the vectors, you can store additional metadata for each vector. This is useful for storing information about the vectors such as the original text, image URL, or any other data that you want to associate with the vectors.
⚙️ Quickstart with Rust
To get started with SahomeDB in Rust, you need to add sahomedb to your Cargo.toml.You can do so by running the command below which will add the latest version of SahomeDB to your project.
cargo add sahomedb
After that, you can use the code snippet below as a reference to get started with SahomeDB. In short, use Collection to store your vector records or search similar vector and use Database to persist a vector collection to the disk.
In short, use Collection to store your vector records or search similar vector and use Database to persist a vector collection to the disk.
use sahomedb::prelude::*;
fn main() {
// Vector dimension must be uniform.
let dimension = 128;
// Replace with your own data.
let records = Record::many_random(dimension, 100);
let mut config = Config::default();
// Optionally set the distance function. Default to Euclidean.
config.distance = Distance::Cosine;
// Create a vector collection.
let collection = Collection::build(&config, &records).unwrap();
// Optionally save the collection to persist it.
let mut db = Database::new("data/test").unwrap();
db.save_collection("vectors", &collection).unwrap();
// Search for the nearest neighbors.
let query = Vector::random(dimension);
let result = collection.search(&query, 5).unwrap();
println!("Nearest ID: {}", result[0].id);
}
Dealing with Metadata
In SahomeDB, you can store additional metadata for each vector which is useful to associate the vectors with other data. The code snippet below shows how to insert the Metadata to the Record or extract it.
use sahomedb::prelude::*;
fn main() {
// Inserting a metadata value into a record.
let data: &str = "This is an example.";
let vector = Vector::random(128);
let record = Record::new(&vector, &data.into());
// Extracting the metadata value.
let metadata = record.data.clone();
let data = match metadata {
Metadata::Text(value) => value,
_ => panic!("Data is not a text."),
};
println!("{}", data);
}
🐍 Quickstart with Python
SahomeDB also provides a Python binding which allows you to add it directly to your project. You can install the Python library of SahomeDB by running the command below:
pip install sahomedb
from sahomedb.prelude import *
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Open the database.
db = Database("data/example")
# Replace with your own records.
records = Record.many_random(dimension=128, len=100)
# Create a vector collection.
config = Config.create_default()
collection = Collection.from_records(config, records)
# Optionally, persist the collection to the database.
db.save_collection("my_collection", collection)
# Replace with your own query.
query = Vector.random(128)
# Search for the nearest neighbors.
result = collection.search(query, n=5)
# Print the result.
print("Nearest neighbors ID: {}".format(result[0].id))
If you want to learn more about using SahomeDB for real-world applications, you can check out the this Google Colab notebook which demonstrates how to use SahomeDB to build a simple image similarity search engine: Image Search Engine with SahomeDB
🎯 Benchmarks
SahomeDB uses a built-in benchmarking suite using Rust's Criterion crate which we use to measure the performance of the vector database.
Currently, the benchmarks are focused on the performance of the collection's vector search functionality. We are working on adding more benchmarks to measure the performance of other operations.
If you are curious and want to run the benchmarks, you can use the following command which will download the benchmarking dataset and run the benchmarks:
cargo bench
Memory Usage
SahomeDB uses HNSW which is known to be a memory hog compared to other indexing algorithms. We decided to use it because of its performance even when storing large datasets of vectors with high dimension.
In the future, we might consider adding more indexing algorithms to make SahomeDB more flexible and to cater to different use cases. If you have any suggestions of which indexing algorithms we should add, please let us know.
Anyway, if you are curious about the memory usage of SahomeDB, you can use the command below to run the memory usage measurement script. You can tweak the parameters in the examples/measure-memory.rs file to see how the memory usage changes.
cargo run --example measure-memory
Quick Results
Even though the results may vary depending on the hardware and the dataset, we want to give you a quick idea of the performance of SahomeDB. Here are some quick results from the benchmarks:
10,000 vectors with 128 dimensions
- Search time: 0.15 ms
- Memory usage: 6 MB
1,000,000 vectors with 128 dimensions
- Search time: 1.5 ms
- Memory usage: 600 MB
These results are from a machine with an Apple M2 CPU and 16 GB of RAM. The dataset used for the benchmarks is a random dataset generated by the Record::many_random function or SIFT datasets with additional random usize as its metadata.
🤝 Contributing
The easiest way to contribute to this project is to star this project and share it with your friends. This will help us grow the community and make the project more visible to others.
If you want to go further and contribute your expertise, we will gladly welcome your code contributions. For more information and guidance about this, please see contributing.md.
If you have deep experience in the space but don't have the free time to contribute codes, we also welcome advices, suggestions, or feature requests. We are also looking for advisors to help guide the project direction and roadmap.
This project is still in the early stages of development. We are actively working on it and we expect the API and functionality to change. We do not recommend using this in production yet.
If you are interested about the project in any way, please join us on Discord. Help us grow the community and make SahomeDB better 😁
Code of Conduct
We are committed to creating a welcoming community. Any participant in our project is expected to act respectfully and to follow the Code of Conduct.
Disclaimer
This project is still in the early stages of development. We are actively working on it and we expect the API and functionality to change. We do not recommend using this in production yet.



