spokes
| Crates.io | spokes |
| lib.rs | spokes |
| version | 0.4.0-rc.4 |
| created_at | 2022-08-02 18:43:42.308725+00 |
| updated_at | 2026-01-22 19:34:44.288709+00 |
| description | A network and network flow library. |
| homepage | |
| repository | https://gitlab.com/schmidmt/spokes |
| max_upload_size | |
| id | 637510 |
| size | 155,891 |
documentation
README
spokes
Network and Network Flow Optimization Tools
Introduction
The following example is based on the following graph
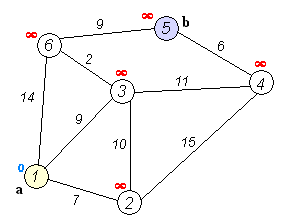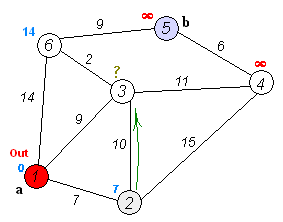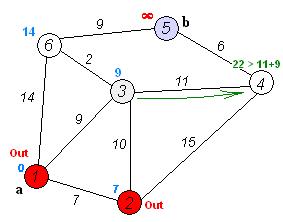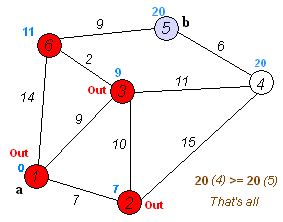 sourced from [Wikipedia][https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dijkstra%27s_algorithm].
sourced from [Wikipedia][https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dijkstra%27s_algorithm].
Here, the goal is to find the shortest path tree rooted at node 0. In the example, it is verified the distance from node 0 to node 4 is 20.
use spokes::{Network, algorithms::{dijkstra_shortest_path, Distance}, ArcStorage};
let mut network: Network<usize, (), u16> = Network::new();
network.add_nodes((0..6).map(|i| (i, ())));
network.add_arcs([
(0, 1, 7), (1, 0, 7),
(0, 5, 14), (5, 0, 14),
(0, 2, 9), (2, 0, 9),
(1, 2, 10), (2, 1, 10),
(1, 3, 15), (3, 1, 15),
(2, 5, 2), (5, 2, 2),
(2, 3, 11), (3, 2, 11),
(3, 4, 6), (4, 3, 6),
(4, 5, 9), (5, 4, 9),
]);
let shortest_path_tree = dijkstra_shortest_path(&network, 0);
assert_eq!(shortest_path_tree.node(&4), Some(&Distance::Finite(20)));
let mut expected_network: Network<usize, Distance<u16>, ()> = Network::new();
expected_network.add_nodes([
(0, Distance::Finite(0)),
(1, Distance::Finite(7)),
(2, Distance::Finite(9)),
(3, Distance::Finite(20)),
(4, Distance::Finite(20)),
(5, Distance::Finite(11)),
]);
expected_network.add_arcs([
(1, 0),
(2, 0),
(3, 2),
(5, 2),
(4, 5),
]);
assert_eq!(shortest_path_tree, expected_network);
License: MIT or Apache-2.0